Section VI discusses intentional discrimination or disparate treatment as one type of Title VI claim. Another type of Title VI violation is based on agency Title VI implementing regulations and is known as the disparate impact or discriminatory effects standard. While a discriminatory impact or effect may also be evidence of intentional discrimination or disparate treatment, this section discusses disparate impact as a cause of action independent of any intent.
The disparate impact regulations seek to ensure that programs accepting federal money are not administered in a way that perpetuates the repercussions of past discrimination. As the Supreme Court has explained, even benignly-motivated policies that appear neutral on their face may be traceable to the nation’s long history of invidious race discrimination in employment, education, housing, and many other areas. See Griggs v. Duke Power Co., 401 U.S. 424, 430–31 (1971); City of Rome v. United States, 446 U.S. 156, 176–77 (1980); Gaston Cty. v. United States, 395 U.S. 285, 297 (1969). The disparate impact regulations ensure “that public funds, to which all taxpayers of all races contribute, not be spent in any fashion which encourages, entrenches, subsidizes, or results in racial discrimination.” H.R. Misc. Doc. No. 124, 88th Cong., 1st Sess. 3, 12 (1963). The Supreme Court explained in Griggs, 401 U.S. at 429–30, that under Title VII, which was enacted at the same time as Title VI, “practices, procedures, or tests neutral on their face, and even neutral in terms of intent, cannot be maintained if they operate to ‘freeze’ the status quo of prior discriminatory employment practices.” Id. at 430; see also Texas Dep’t of Hour. & Cmty. Affairs v. Inclusive Communities, 135 S. Ct. 2507, 2521 (2015) (noting that “[r]ecognition of disparate impact claims is consistent with the [Fair Housing Act’s] central purpose” as it “was enacted to eradicate discriminatory practices within a sector of our Nation’s economy”) (citations omitted). The regulations task agencies to take a close look at neutral policies that disparately exclude minorities from benefits or services, or inflict a disproportionate share of harm on them.
A growing body of social psychological research has also reaffirmed the need for legal tools that address disparate impact. This research demonstrates that implicit bias against people of color remains a widespread problem .[1] Such bias can result in discrimination that federal agencies can prevent and address through enforcement of their disparate impact regulations. Because individual motives may be difficult to prove directly, Congress has frequently permitted proof of only discriminatory impact as a means of overcoming discriminatory practices. The Supreme Court has, therefore, recognized that disparate impact liability under various civil rights laws, “permits plaintiffs to counteract unconscious prejudices and disguised animus that escape easy classification as disparate treatment.” Id. at 2522.
In a disparate impact case, the investigation focuses on the consequences of the recipient’s practices, rather than the recipient’s intent. Lau v. Nichols, 414 U.S. 563, 568 (1974). As explained throughout this Section, “a plaintiff bringing a disparate-impact claim challenges practices that have a ‘disproportionately adverse effect on minorities’ and are otherwise unjustified by a legitimate rationale.” Inclusive Communities, 135 S. Ct. at 2513 (quoting Ricci v. DeStefano, 557 U.S. 557, 577 (2009). [2]
Twenty-six federal funding agencies have Title VI regulations that include provisions addressing the disparate impact or discriminatory effects standard. [3]
AGENCY TITLE VI DISPARATE IMPACT REGULATIONS
A recipient, in determining the type of disposition, services, financial aid, benefits, or facilities which will be provided under any such program, or the class of individuals to whom, or the situations in which, such will be provided under any such program, or the class of individuals to be afforded an opportunity to participate in any such program, may not, directly or through contractual or other arrangements, utilize criteria or methods of administration which have the effect of subjecting individuals to discrimination because of their race, color, or national origin, or have the effect of defeating or substantially impairing accomplishment of the objectives of the program as respects individuals of a particular race, color, or national origin.
See , e.g. , 28 C.F.R. § 42.104(b)(2) (emphasis added)(DOJ regulations).
The Supreme Court has repeatedly held that Title VI regulations validly prohibit practices having a discriminatory effect on protected groups, even if the actions or proactices are not intentionally discriminatory. Guardians Ass’n v. Civil Serv. Comm’n, 463 U.S. 582, 643 (1983) (Stevens, J., dissenting) (citing Lau, 414 U.S. at 568, 571 (Stewart, J., concurring) and Fullilove v. Klutznick, 448 U.S. 448, 479 (1980) (opinion of Burger, C.J.)); Alexander v. Choate, 469 U.S. 287, 293 (1985)). Funding agencies require that entities receiving federal financial assistance enter into standard agreements or provide assurances that the recipient will comply with the funding agency’s implementing regulations under Title VI. See, e.g., 28 C.F.R. § 42.105 (DOJ) (requiring applications for federal financial assistance to be accompanied by an assurance of compliance with Title VI implementing regulations); see also United States v. Marion Cty Sch. Dist., 625 F.2d 607, 609, 612–13 (5th Cir. 1980) (confirming legitimacy of assurance requirement); Guardians, 463 U.S. at 642 n.13 (Stevens, J., dissenting) (quoting from HUD assurance). [4]
The basic analytical framework for applying the disparate impact standard has remained unchanged for decades; how to prove a violation of the disparate impact standard is discussed below.
B. Sandoval and the Critical Role of the Federal Funding Assistance
Federal funding agencies play a vital role in enforcing the prohibition on disparate impact discrimination through complaint investigations, compliance reviews, and guidance on how to comply with Title VI. In 1994, the Attorney General directed the “Heads of Departments and Agencies” to “ensure that the disparate impact provisions in your regulations are fully utilized so that all persons may enjoy equally the benefits of federally financed programs. [5] The memorandum stated that agency enforcement “is an essential component of an effective civil rights compliance program.… Frequently, discrimination results from policies and practices that are neutral on their face but have the effect of discriminating[.] Those policies and practices must be eliminated unless they are shown to be necessary to the program’s operation and there is no less discriminatory alternative.” Id. (emphasis added).
The agencies’ critical role only increased after the Supreme Court’s 2001 decision in Alexander v. Sandoval, 532 U.S. 275 (2001). Before Sandoval, it was believed that individuals could file civil actions relying on the Title VI disparate impact standard. In Sandoval, however, the Supreme Court held that individuals did not have a right of action to enforce the Title VI disparate impact regulations in federal court. Id. at 293. Following Sandoval, the Civil Rights Division issued a memorandum on October 26, 2001, for “Heads of Departments and Agencies, General Counsels and Civil Rights Directors” that clarified and reaffirmed federal government enforcement of the disparate impact regulations. The memorandum explained that although Sandoval foreclosed private judicial enforcement of Title VI the regulations remained valid and funding agencies retained their authority and responsibility to enforce them.[6] Nor does Sandoval affect the disparate impact provisions of other laws, such as Title VII or the Fair Housing Act. The agencies’ Title VI disparate impact regulations continue to be a vital administrative enforcement mechanism.
Complaint investigations and compliance reviews. In addition to the administrative complaint process, federal funding agencies are authorized to initiate affirmative compliance reviews as a mechanism for ensuring recipient compliance. Federal funding agencies should prioritize vigorous enforcement of their Title VI disparate impact provisions both through investigation of complaints and through compliance reviews.
Agency guidance. Funding agencies buttress their enforcement role by providing informal and formal guidance clarifying and applying their Title VI disparate impact regulations. The Supreme Court has stated that agencies have a great deal of discretion in establishing discriminatory impact standards: “Title VI had delegated to the agencies in the first instance the complex determination of what sorts of disparate impact upon minorities constituted sufficiently significant social problems, and were readily enough remediable, to warrant altering the practices of the federal grantees that had produced those impacts.” Choate, 469 U.S. at 293–94; see also Sandoval, 532 U.S. at 306 (Stevens, J., dissenting). And lower courts have consistently recognized and deferred to agency interpretations of the disparate impact standard. See, e.g., United States v. Maricopa Cty, 915 F. Supp. 2d 1073, 1080 (D. Ariz. 2012) (citing Auer v . Robbins, 519 U.S. 452, 461 (1997)) (agency interpretation of its own regulations “controlling unless plainly erroneous or inconsistent with the regulations”); S. Camden Citizens in Action v . N.J. Dep’t of Envtl. Prot., 145 F. Supp. 2d 446, 496 (D.N.J. 2001) (reviewing Environmental Protection Agency regulations, guidance, and administrative decisions in analyzing claim brought under EPA’s disparate impact provision); opinion modified and supplemented, 145 F. Supp. 2d 505 (D.N.J.), rev’d on other grounds, 274 F.3d 771 (3d Cir. 2001).
C. Proving a Violation of the Disparate Impact Standard
Understanding the process for establishing Title VI noncompliance in disparate impact cases is crucial in assessing an allegation or matter and determining how an agency conducts its investigation. Courts have developed analytical frameworks to assess disparate impact claims in litigation that inform agencies’ investigative processes. In some instances, agencies have issued guidance documents articulating a process for determining compliance in particular types of disparate impact cases.
The elements of a Title VI disparate impact claim are similar to the analysis of cases decided under Title VII. N.Y. Urban League, Inc. v. New York, 71 F.3d 1031, 1036 (2d Cir. 1995).[7] Cases decided under the Fair Housing Act, 42 U.S.C. § 3601 et seq., also often employ disparate impact analyses, and HUD’s Fair Housing Act implementing regulations, 24 C.F.R. § 100.500, adopt a formulation of the disparate impact standard that is substantially similar to the Title VI and Title VII standard.
Courts have adopted a three-part test to determine whether a recipient’s policy or practice violates the Title VI disparate impact regulations. First, does the adverse effect of the policy or practice disproportionately affect members of a group identified by race, color, or national origin? Some courts refer to this first inquiry as the “prima facie” showing. If so, can the recipient demonstrate the existence of a substantial legitimate justification for the policy or practice? N.Y. Urban League, 71 F.3d at 1036. A violation is still established if the record shows the justification offered by the recipient was pretextual. See Elston v. Talladega Cty. Bd. of Educ., 997 F.2d 1394, 1407 (11th Cir. 1993) (citing Georgia State Conf. v. Georgia, 775 F.2d 1403, 1417 (11th Cir. 1985)). Finally, is there an alternative that would achieve the same legitimate objective but with less of a discriminatory effect? If such an alternative is available to the recipient, even if the recipient establishes a justification, the policy or practice will still violate disparate impact regulations.
TITLE VI DISPARATE IMPACT VIOLATION
In administrative investigations, this court-developed burden shifting framework serves as a useful paradigm for organizing the evidence. Agency investigations, however, often follow a non-adversarial model in which the agency collects all relevant evidence then determines whether the evidence establishes discrimination. Under this model, agencies often do not shift the burdens between complainant and recipient when making findings. For agencies using this method, the following sections serve as a resource for conducting an investigation and developing an administrative enforcement action where appropriate.
AGENCY PRACTICE TIP
Agencies need not address each element in rank order because lack of evidence of any one of these elements results in a “no violation” finding and concludes the analysis. However, in many cases understanding the nature of the harm is an important first step to evaluating its impact on a protected class. The sections below provide additional insight into the potential benefits of proceeding in a particular order through the investigation and analysis.
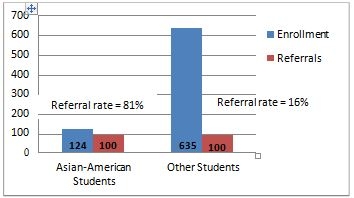
The example below, adapted from Department of Education guidance, illustrates how the three- part test would inform an administrative investigation of a Title VI complaint alleging that a school discipline policy violates the disparate impact regulation .[8]
ILLUSTRATION: DISPARATE IMPACT INVESTIGATION OF SCHOOL DISCIPLINARY POLICY
A middle school has a “zero tolerance” tardiness policy. Students who are more than five minutes tardy to class are always referred to the principal’s office at a particular school, where they are required to remain for the rest of the class period regardless of their reason for being tardy. The school also imposes an automatic one-day suspension when a student is recorded as being tardy five times in the same semester. Additional tardiness results in longer suspensions and a meeting with a truancy officer. The evidence shows Asian-American students are disproportionately losing instruction time under the school’s “zero tolerance” tardiness policy, as a result of both office referrals and suspensions for repeated tardiness.

An investigation further reveals that white and Hispanic students are more likely to live within walking distance of the school, while Asian-American students are more likely to live farther away and in an area cut off by an interstate highway that prevents them from walking to school. The majority of Asian- American students are thus required to take public transportation. These students take the first public bus traveling in the direction of their school every morning. Even though they arrive at the bus stop in time to take the first bus available in the morning, they often are not dropped off at school until after school has begun.
As justification for the “zero tolerance” tardiness policy, the school articulates the goals of reducing disruption caused by tardiness, encouraging good attendance, and promoting a climate where school rules are respected, all of which the federal funding agency accepts as important educational goals. The agency would then assess the fit between the stated goals and the means employed by the school— including whether the policy is reasonably likely to reduce tardiness for these students under these circumstances .
Assuming there was such a fit, the agency would then probe further to determine the availability of alternatives that would also achieve the important educational goals while reducing the adverse effect on Asian-American students (e.g., aligning class schedules and bus schedules, or excusing students whose tardiness is the result of bus delays). If the agency determines that a school’s articulated goal can be met through alternative policies that eliminate or have less of an adverse racial impact, the agency would find the school in violation of Title VI and require that the school implement those alternatives.
1. Establishing an Adverse Disparate Impact
The first step in analyzing any disparate impact case is determining whether the recipient’s criteria or method of administering its programs or activities adversely and disparately affect members of a protected class. In some cases federal agencies proceed directly to preliminary findings after this step. To establish an adverse disparate impact, the investigating agency must (1) identify the specific policy or practice at issue; (2) establish adversity/harm; (3) establish significant disparity; [9] and (4) establish causation. See N.Y.C. Envtl. Justice All. v. Giuliani, 214 F.3d 65, 69 (2d Cir. 2000) (plaintiffs must “allege a causal connection between a facially neutral policy and a disproportionate and adverse impact on minorities.”).
ELEMENTS TO ESTABLISH ADVERSE DISPARATE IMPACT UNDER TITLE VI
a. Identifying the facially neutral policy or practice
Accurate disparate impact analyses begin with identifying the policy or practice that allegedly caused the disparate harm. Inclusive Communities, 135 S. Ct. at 2523 (“a disparate-impact claim that relies on a statistical disparity must fail if the plaintiff cannot point to a defendant’s policy or policies causing that disparity”). Although plaintiffs’ claims succeed or fail based on whether they have established adversity/harm, significant disparity, and causation, identifying the policy at issue in forms the evaluation of the evidence put forth at these three stages.
When analyzing disparate impact claims, investigating agencies must accurately and completely define the policy or practice at issue. In some cases, the agency will have to broaden its inquiry beyond the specific complaint allegations in order to conduct this analysis. Courts, however, provide little guidance to agencies in how to separate discrete parts of a recipient’s evaluation process. Identifying the relevant parts of any policy or practice is a fact-specific inquiry.
AGENCY PRACTICE TIP
While an investigating agency must initially identify the full policy or practice at issue, this does not mean the agency must investigate every application of that practice. For example, in statewide or large–scale investigations, agencies may develop evidentiary sampling methods probative of the merits of such complaints. Sampling methods are discussed further in the disparity section below.
One method to discern whether the legally relevant policy or practice is broader than the action identified by the complainant involves identifying the negative effect that the challenged action has on the protected group. For example, in New York City Environmental Justice Alliance, the court rejected a challenge to New York City’s decision to scale back a community garden program benefitting minority neighborhoods. Although the precise action challenged was the City’s closing or selling of community gardens, the plaintiffs identified the negative effect of the action as the reduction of the amount of open space/green space available to minority community districts. 214 F.3d at 71. The court saw the issue as the City’s overall policy about green spaces, not its decision to sell or close community gardens. So viewed, the City would not violate Title VI unless the overall open space/green space policy disadvantaged predominantly minority neighborhoods significantly more than predominantly white neighborhoods. The plaintiffs’ statistics only included calculations that compared available space from community gardens, parks, and playgrounds, and excluded space from regional parks available to the community districts. Id.
The court noted that this exclusion meant that they could not actually evaluate the City’s overall green space policy: “[T]he plaintiffs fail to explain how ‘open space’ statistics excluding regional parks adjacent to minority communities—some of the most important open spaces in the City—are meaningful in determining whether, as they assert, there is a disparate impact in minority communities as a whole resulting from the City’s sale of garden lots.” Id. at 71 n.5.
Similarly, in Greater New Orleans Fair Housing Action Center v. HUD, 639 F.3d 1078 (D.C. Cir. 2011), the court rejected a challenge to one part of HUD’s formula for awarding hurricane relief grants. The plaintiffs alleged that under HUD’s formula, African Americans had less access to rebuilding programs after hurricanes Katrina and Rita. Id. at 1079. The court held that while that one part of the formula, viewed in isolation from the rest, may have had an adverse impact on African Americans, other parts of the formula may have disproportionately benefitted African Americans. Id. at 1086. Thus, the court looked at the Katrina/Rita grant process as a whole. Id. The court also rejected plaintiffs’ evidence that was limited to a single parish because HUD applied the formula in a much broader geographic area. Id .
The Greater New Orleans court’s focus on the geographic area where the impact occurred provides a related method to ascertain the policy or practice. Specifically, agencies should identify the area where the negative effects occur even if that area is larger than the area that is the focus of the complainant’s allegation. For example, in Coalition of Bedford-Stuyvesant Block Ass’n v. Cuomo, 651 F. Supp. 1202, 1206 (E.D.N.Y. 1987), the plaintiffs claimed the City of New York located shelters for homeless persons in a manner that had the effect of concentrating all but one of the City-owned homeless shelters in Brooklyn’s minority communities in violation of, inter alia, the Fourteenth Amendment. The court, however, considered all of the sites City- wide, and not in Brooklyn, because the relevant policy and practice was the City’s siting of shelters generally, not just in one portion of its jurisdiction. Id. at 1209. The court rejected plaintiff’s data because it only covered the impact in Brooklyn. Id.
AGENCY PRACTICE TIP
Agencies should inquire about the challenged action’s negative effect—looking at who is impacted and where the impact occurs—in order to identify the legally relevant policy or practice. Agencies should remember that the answer to this question may also come from the disparity/discriminatory effect analysis discussed below.
The importance of avoiding examination of only a portion of the legally relevant policy or practice does not mean that an agency must always examine the entirety of what a recipient does. Where plaintiffs allege discrimination in access or opportunities instead of in outcomes, a policy or portion of that policy can have a discriminatory effect on a protected class even where another policy or portion of that policy has a countervailing effect. As the Supreme Court has stated in the employment context, because a certain group ultimately gets hired or promoted at the same rate as another overall does not preclude claims that some aspect of the hiring or promotion process has a disparate impact on them. See Connecticut v. Teal, 457 U.S. 440, 451–52 (1982); accord Clady v. Cty. of Los Angeles, 770 F.2d 1421, 1429 (9th Cir. 1985). The Teal Court made clear that Title VII ensures equal opportunities for individuals, not just equal outcomes for groups. 457 U.S. at 451. In Teal, the defendant imposed a written examination for promotion candidates that excluded a much greater number of African Americans. It then employed affirmative action with respect to those who did pass to ensure that it promoted a proportionate number of African American candidates. See id. at 443–44. The Court held that those whom the test excluded from consideration were entitled to challenge the discriminatory procedure under Title VII, notwithstanding the absence of racial disparity in the “bottom-line,” i.e., the final award of promotions. Id. at 451, 456.
The Teal holding has been applied in Fair Housing Act cases relating to access to nondiscriminatory housing, Betsey v. Turtle Creek Assoc., 736 F.2d 983, 987 (4th Cir. 1984) (“‘Bottom-line’ considerations of the number and percentage of minorities in the rest of the complex or community are ‘of little comfort’ to those minority families evicted from Building Three”), and Title VI disparate impact cases relating to access to schools or school programs. See, e.g., Cureton v. NCAA, 37 F. Supp. 2d 687, 704–05 (E.D. Pa. 1999) (rejecting NCAA’s “bottom-line” defense that pointed to graduation rates in disparate impact case involving initial eligibility standards), rev’d on other grounds, 198 F.3d 107 (3d Cir. 1999); Elston, 997 F.2d at 1418–20 (finding the increase in the racial identifiability of black-majority school as a result of school transfer practices sufficient to constitute a disparate impact, even if overall racial balances had not changed in either the county or county school system, because the success of desegregation is measured on a school-by-school basis).
Finally, the importance of identifying a specific practice does not necessarily mean that practice must be affirmatively undertaken; sometimes the relevant policy or practice could be the failure to do something, or even the failure to have a policy. In other words, inaction can exert a disproportionate adverse effect. Language access cases provide an example. The failure to have a coherent language assistance policy, or to train employees on providing assistance, can prevent individuals who are limited English proficient from benefiting from the recipient’s program. Where a recipient does not implement any language assistance policy but instead leaves these individual employees untrained and uninformed to do what they will, the result may be that these employees will often fail to provide appropriate assistance. See, e.g., Maricopa Cty., 915 F. Supp. 2d at 1079 (disparate impact violation based on national origin properly alleged where recipient “failed to develop and implement policies and practices to ensure [limited English proficient] Latino inmates have equal access to jail services” and discriminatory conduct of detention officers was facilitated by “broad, unfettered discretion and lack of training and oversight” resulting in denial of access to important services). Similarly, where law enforcement agencies fail to train their officers, a failure to properly assist persons who are limited English proficient often follows. See, e.g., U.S. v. Town of E. Haven, No. 3:12–cv–1652, 2012 WL 5869974, ¶ 43 (D. Conn. filed Nov. 20, 2012).
b. Establishing adversity/harm
Once the investigating agency has accurately identified the policy or practice, it must evaluate whether the policy or practice “harms” a particular group of people enough to be actionable. This element is sometimes referred to as “adversity of the impact.” [10] The investigating agency must determine whether the alleged consequences are sufficiently adverse or harmful. See Bryan v . Koch, 627 F.2d 612, 617 (2d Cir. 1980). Adversity exists if a fact specific inquiry determines that the nature, size, or likelihood of the impact is sufficient to make it an actionable harm. This discussion will use the terms “adversity” and “harm” interchangeably.
Most cases applying the Title VI disparate impact standard do not explicitly address adversity as a separate element. Rather, courts frequently assume that the impacts alleged were sufficiently adverse, impliedly recognizing a wide range of harms, including physical, economic, social, cultural, and psychological. In many administrative investigations, particularly those involving the denial of services or benefits, investigating agencies, too, will be able easily to conclude the harm alleged is legally sufficient.
The expansive language of Title VI and its implementing regulations support this approach: the statute states that no person shall on the ground of race, color, or national origin “be excluded from participation in, be denied the benefits of, or be subjected to discrimination under any program or activity receiving Federal financial assistance.” 42 U.S.C. § 2000d. In implementing this provision, agency regulations further state that recipients may not administer their programs or activities in a manner which “den[ies] any individual any disposition, service, financial aid, or benefit provided under the program.” 28 C.F.R. § 42.104(b)(1)(i) (DOJ) (emphasis added), or “restrict[s] an individual in any way in the enjoyment of any advantage or privilege enjoyed by others receiving any disposition, service, financial aid, or benefit under the program,” Id. § 42.104(b)(1)(iv) (emphasis added). Agency disparate impact regulations do not define discriminatory “effects” but simply state that recipients may not “utilize criteria or methods of administration which have the effect of subjecting individuals to discrimination because of their race, color, or national origin ….” Id. § 42.104(b)(2). [11]
AGENCY PRACTICE TIP
While establishing adversity in most cases presents a low bar, investigating agencies nevertheless should employ a broad definition of adversity/harm, and gather any and all evidence of adversity/harm or risk of adversity/harm, including anecdotal evidence from complaining witnesses. Even though such additional evidence may not be required as a legal matter, it provides important context for the decision–maker. Such evidence also informs development of the appropriate remedy in the case of noncompliance.
Fewer or inferior services or benefits. Courts have frequently identified Title VI adversity/harm where recipients’ policies or practices result in fewer services or benefits, or inferior service or benefits. In this type of case, the recipient denies the plaintiff something deemed desirable. For example, in Larry P. v. Riles, 793 F.2d 969 (9th Cir. 1986), the court held that improper placement in special education classes had a “definite adverse effect” because such “classes are dead-end classes which de-emphasize academic skills and stigmatize children improperly placed in them.” Id. at 983; see also Elston, 997 F.2d at 1412 (holding that stigmatization of black children and the risk of closure of a school in a black community, among other things, “might well constitute a disparate impact”). While these cases often arise in the education context, many different types of inferior services and benefits will satisfy the adversity requirement. See, e.g., Meek v. Martinez, 724 F. Supp. 888, 906 (S.D. Fla. 1987) (minority seniors harmed when receiving less financial aid for community services than non- minority peers); Campaign for Fiscal Equity, Inc. v. New York, 86 N.Y.2d 307, 323–24, 655 N.E.2d 661, 631 N.Y.S.2d 565 (1995) (adversity properly alleged where minority students received less state financial aid as a group and per pupil than their nonminority peers); Sandoval v. Hagan, 197 F.3d 484, 508 (11th Cir. 1999) (lack of drivers’ licenses adversely affects individuals in the form of lost economic opportunities, social services, and other quality of life pursuits), rev’d on other grounds sub nom. Alexander v. Sandoval, 532 U.S. 275 (2001); Maricopa Cty., 915 F. Supp. 2d at 1081 (adversity properly alleged where limited English proficient Latino inmates had diminished access to jail services such as sanitary needs, food, clothing, legal information, and religious services).
Distribution of burdens, negative effects. Recipient practices also can harm protected class members even without the loss of specific services or benefits. In this type of case, the recipient distributes burdens, or something seen as undesirable. For example, in Coalition of Concerned Citizens Against I-670 v. Damian, 608 F. Supp. 110, 127 (S.D. Ohio 1984), the court held that disruptions and other impacts of planned highway construction would negatively affect minority residents living in the area under construction. In another case, a court found that plaintiffs established sufficient potential harm to their health resulting from the recipient’s issuance of air pollution permits for a cement processing facility, noting that the operation of the facility would “adversely affect [the plaintiffs’] health to a degree that meets the standard of ‘adversity’ under Title VI.” S. Camden Citizens in Action v. N.J. Dep’t of Envtl. Prot., 145 F. Supp. 2d 446, 490, opinion modified and supplemented, (D.N.J.), rev’d on other grounds, 274 F.3d 771 (3d Cir. 2001). The court granted a preliminary injunction and the air permits were vacated. Id. at 505; see also Darensburg v. Metro. Transp. Comm., 636 F.3d 511, 520–22 (9th Cir. 2011), (finding that while plaintiffs had not established a prima facie case, a transit expansion plan could result in disproportionate harm to minorities); Maricopa Cty., 915 F. Supp. 2d at 1079 (plaintiff properly stated a disparate impact claim where Latinos, as compared with non-Latinos, were far more likely to be stopped by officers).
Threatened or imminent harm. These cases and others also illustrate that threatened or imminent harm may satisfy the adversity requirement. [12] See, e.g., NAACP v. Med. Ctr., Inc., 657 F.2d 1322, 1332–38 (3d Cir. 1981) (en banc) (examining a disparate impact claim under Title VI concerning the future impact of a planned medical center relocation); Damian, 608 F. Supp. at 127 (examining a disparate impact claim brought under Title VI concerning the future impact of a planned highway expansion). Notably, the Environmental Protection Agency has determined that based on a technical analysis, a showing of potential health effects, depending on their nature and severity (e.g., cancer risk), provides an adequate basis for a finding of adversity under EPA’s disparate impact regulation. EPA Investigative Report, For Title VI Admin. Complaint File No. 16R ‐ 99 ‐ R9, at 26–28 (Aug. 25, 2011); [13] EPA Draft Revised Guidance for Investigating Title VI Administrative Complaints Challenging Permits (Draft Revised Investigation Guidance), 65 Fed. Reg. 39,650, 39,679–81 (June 27, 2000).
Mix of costs and benefits, effects that are difficult to quantify. In some cases, recipient actions provide a mix of costs and benefits, or the alleged harm may be difficult to quantify.
These factors may increase the complexity of the adversity/harm analysis. For example, hospital relocations and closures are often challenged on the grounds that they will force residents of predominantly minority neighborhoods to travel greater distances for service, without an attempt to demonstrate that this would cause a hardship or that the quality of service and care would be diminished. In Bryan, 627 F.2d at 617, the court addressed a challenge to the closure of a hospital that served a 98% minority population, compared with a 66% minority population in the surrounding city’s hospital system. Based on these statistics, the court easily found the closure would affect the minority population disproportionately (this step of the analysis—disparity—is discussed in C.1.c. below). Less easy was “whether the impact of this disparity is sufficiently adverse to create a prima facie Title VI violation ….” Id. The court pointed out that the great majority of patients would be provided satisfactory care in nearby municipal and voluntary hospitals, and only a small number of emergency room patients “would suffer adverse consequences if the nearest emergency room treatment available were at even slightly more distant locations.” Id. Ultimately, the court proceeded with the subsequent steps of the impact analysis instead of stopping the analysis based on the weakness of the adversity/harm evidence.
Similarly, in a school closing case, the plaintiffs alleged that the closure and student transfers resulted in a discriminatory effect on Hispanic students by depriving them of the high quality education previously provided. The court found there was no adversity/harm, and thus declined to analyze disparity, because (1) the new schools had comparable facilities, (2) there was no evidence that the new schools would be overcrowded, (3) special education programs would continue at the new schools, and (4) the new schools had similarly high percentages of at-risk and minority students. Villanueva v. Carere, 85 F.3d 481, 487 (10th Cir. 1996).[14]
Determining the sufficiency of harm can be a fact-intensive and complicated inquiry, particularly where recipient actions provide both costs and benefits, or where the alleged harm can be difficult to quantify. In NAACP v. Medical Center, the court noted that it was a close call whether impacts were sufficiently adverse/harmful. Here, the court questioned (without deciding) the plaintiffs’ contention that a hospital’s relocation from the inner city to an outlying suburban location caused sufficient harm absent proof that the need to travel a few extra miles inflicted significant harm on patients. At trial, the district court considered whether relocation would result in a slight increase in travel time, a modest decrease in the ability of inner city residents to visit patients at the new suburban site, the possibility that a few high risk patients might miss appointments, and the rare chance that treatment would be inadequate. It then determined these to be such unlikely effects that they failed to establish a prima facie case, particularly when weighed against the numerous benefits of the relocation. NAACP v. Wilmington Med. Ctr., 491 F. Supp. 290, 337 (D. Del. 1980). Although the Third Circuit affirmed without deciding this particular issue, a concurrence addressed the issue directly, finding the countervailing benefits accruing to minority patients a determinative consideration:
[T]hese specific findings are part of a larger mosaic: the trial court’s overarching finding that the level of care for all population groups will improve as a result of the benefits that greater consolidation, better-trained residents and upgraded facilities will confer. Measured against [agency] regulations which define Title VI violations as actions which have “the effect of defeating or substantially impairing accomplishment of the objective of the program as respect (sic) individuals of a particular race, color, or national origin,” 45 C.F.R. § 80.3(b)(2) (emphasis added), these de minimis impacts simply do not pass muster.
Med. Ctr., 657 F.2d at 1340 (Adams, J., concurring); see also United States v. Bexar Cty., 484 F. Supp. 855, 859 (W.D. Tex. 1980) (finding the increased quality of care at a new medical center “much more than offset and outweigh” possible transportation problems created by relocation).
In both Medical Center and Bexar, the recipients had taken actions to mitigate the impacts on minorities, and both holdings recognized these efforts as important considerations. In Medical Center, the recipient had entered into an agreement with the Department of Health, Education & Welfare (predecessor to the Department of Health and Human Services), obligating it to “designate an ombudsman to receive and act upon complaints of discrimination, to adopt a system of inpatient utilization control, to prevent either [of the two hospitals in the parent system] from becoming racially identifiable,” and to set aside nearly three million dollars for the renovation of the existing facility. Med. Ctr., 657 F.2d at 1331–32. In Bexar, the hospital understood the new travel burden and had taken steps to alleviate problems by providing mini- bus service. Bexar,484 F. Supp. at 860. It is possible that the court may have ruled differently but for these ameliorative measures.
AGENCY PRACTICE TIP
Investigating agencies should consider the sufficiency of the adversity/harm and carefully consider whether benefits to the affected group offset or outweigh the harms to that group. Agencies should remember that recipients may be able to ensure compliance with Title VI by mitigating any adverse harm that may affect the protected group. Informal resolution efforts often involve identification of mitigation efforts which, if applied, would result in compliance with Title VI by reducing or eliminating adversity/harm.
c. Establishing disparity
An investigating agency’s disparity analysis must answer the question that is the essence of a violation of agency disparate impact regulations: Is a disproportionate share of the adversity/harm borne based on race, color, or national origin? If so, a disparity is established.
To establish a disparity, an investigating agency must use an “appropriate measure.” N.Y.C. Envtl. Justice All., 214 F.3d at 70 (citation omitted). A typical disparity measure involves a comparison between the proportion of persons in the protected class who are adversely affected by the challenged practice and the proportion of persons not in the protected class who are adversely affected. Tsombanidis v. W. Haven Fire Dep’t, 352 F.3d 565, 576–77 (2d Cir. 2003). A disparity is established if the challenged practice adversely affects a significantly higher proportion of protected class members than non-protected class members. Id.
AGENCY PRACTICE TIP
There is no one-size-fits-all measure for disparity. Investigating agencies must tailor their methodology to the circumstances in each case in order to ensure an accurate measurement. For example, under the Fair Housing Act, HUD noted that deciding whether “a particular practice results in a discriminatory effect is a fact–specific inquiry” and that because there are “numerous and varied practices and wide variety of private and governmental entities covered by the Act, it would be impossible to specify in the rule the showing that would be required to demonstrate a discriminatory effect in each of these contexts.” Implementation of the Fair Housing Act’s Disparate Impact Standard, 78 Fed. Reg. 11,460, 11,468, (Feb. 15, 2013). Where recurring case types have sufficient commonalities, however, agencies can consider crafting guidelines for measuring and defining adverse disparate impact in their recipients’ programs. Where such guidelines apply, the investigating agency should, of course, use the methodologies developed for specific matters.
When beginning a disparity analysis, an investigating agency should take two initial steps. First, the agency should identify the protected class. Second, the agency must evaluate whether statistical evidence is available and necessary to evaluate the claim. Next, the agency takes the third and fourth steps, which are the most critical components of the disparity analysis. In the third step, the agency should evaluate on what population the adverse disparate impact must be shown. This highly fact-specific inquiry involves accurately identifying the adversely affected population as well as determining the legally relevant population base from which to draw a comparison population. Finally, the agency must determine whether the disparity shown is sufficiently large to impose legal liability (sometimes termed “practical significance”).
i. Identifying the Protected Class
Typically, the relevant protected class will be evident from the complaint because it alleges harm to a specific group (e.g., “Latinos” or “Blacks”). Other times, however, the complaint may broadly allege harm to “minorities” or to several specific groups collectively, or funding agencies may wish to conduct compliance reviews addressing impacts on such groups in the aggregate. Agencies may conduct disparity analyses in which multiple protected groups are aggregated. Such aggregation is commonplace and presumptively accepted by the courts. See, e.g., Wards Cove Packing Co. v. Atonio , 490 U.S. 642, 650–55 (1989) (conducting a close critique of the statistics used to compare “white” and “nonwhite” workers and indicating that to prove disparate impact, one must provide statistics of probative value comparing “white” and “nonwhite” individuals under Title VII); Darensburg, 636 F.3d at 520–21 (critiquing the district court’s statistical methodology comparing effects on “minorities” and “non-minorities” generally under Title VI while raising no complaint with the aggregate statistics used). Many cases accept statistics aggregating “Blacks” and “Hispanics.” E.g., N.Y.C. Transit Auth. v. Beazer , 440 U.S. 568, 584–85 (1979); Biondo v. City of Chicago, 382 F.3d 680, 682–83 (7th Cir. 2004); Cox v. City of Chicago , 868 F.2d 217, 220 (7th Cir. 1989); Huntington Branch, NAACP v. Town of Huntington, 844 F.2d 926, 929 (2d Cir. 1988), aff’d in part, 488 U.S. 15 (1988).
On the other hand, agencies should avoid aggregation where two groups are not similarly situated and aggregation may hide disproportionate effects on one of the groups. See Rich v. Martin Marietta Corp., 522 F.2d 333, 346 (10th Cir. 1975) (aggregating group statistics as between “blacks, women and Chicanos and [Asians] and American Indians” was inappropriate because the practice “rendered the statistics useless, particularly in view of the fact that the [Asians] especially were heavily represented in the upper echelon of the labor force”).
AGENCY PRACTICE TIP
If the recipient’s policy or practice exerts an adverse/harmful effect on more than one protected group, agencies may aggregate protected groups unless the groups are not similarly situated.
ii. Determining the Need for Statistical Evidence
Often a disparity can be quantified using statistical evidence. See Darensburg, 636 F.3d at 519 (explaining that appropriate statistical evidence can provide a “reliable indicator of a disparate impact” (citing New York Urban League , 71 F.3d at 1038)). And the majority of contemporary disparate impact claims involve comparative evidence based on statistical analysis. It is important to remember, however, that even where statistical evidence is available, circumstantial evidence can be a critical supplement. As the Supreme Court has cautioned, the usefulness of statistics “depends on all of the surrounding facts and circumstances.” Int’l Bhd. of Teamsters v. United States , 431 U.S. 324, 340 (1977).
While statistical evidence is often necessary, in some cases statistical evidence may not be needed. Thomas v. Washington Cty. Sch. Bd. , 915 F.2d 922, 926 (4th Cir. 1990) (“although disparate impact cases usually focus on statistics, they are neither the exclusive nor a necessary means of proof”) (citation omitted). The requisite unfair share of harm can also be shown by evidence of impact on specific individuals. See, e.g., McCoy v. Canterbury , No. 3:10–0368, 2010 WL 5343298, at *5 (S.D.W. Va. Dec. 20, 2010) (a “series of discrete episodes” of the challenged practice can “raise a plausible inference that it has a discriminatory impact on minorities”), aff’d, 428 Fed. App’x 247 (4th Cir. 2011); Mitchell v. Bd. of Trustees, 599 F.2d 582, 585–86 (4th Cir. 1979) (affirming district court’s finding of disparate impact “on the basis of the few specific applications of the policy proven, such inferences of likely other applications as these instances could rationally support, and judicial notice of the world as it is and as it is known in common experience to be”).
The disparate effect of a recipient’s policy or practice is sometimes so obvious or predictable that comparative statistics are simply unnecessary to draw the requisite connection between the policy and harm to a Title VI protected group. For instance, certain recipient language policies have the self-apparent effect of excluding individuals based on their national origin. See Lau v. Nichols, 414 U.S. 563, 568 (1974) (finding national origin discrimination without reliance on statistical evidence because instruction takes place only in English and therefore “[i]t seems obvious that the Chinese-speaking minority receive fewer benefits than the English-speaking majority”); see also Mitchell, 599 F.2d at 585–86 (upholding district court finding that “a policy that arguably would not renew the contract of any teacher who for any reason could not commit at contract renewal time to a full year’s uninterrupted service, but that singled out pregnancy alone for compelled disclosure, would necessarily impact disproportionately upon women”).
AGENCY PRACTICE TIP
Agencies should not immediately dismiss a claim if statistics are not provided or available. Instead, agencies should ask if the requisite unfair share of harm can also be shown by evidence of impact on specific individuals or if the discriminatory effect of a recipient’s policy or practice is inherently obvious or predictable.
iii. Relevant Comparator Population
If an agency uses statistical evidence, it must determine the particular proportion of protected persons and non-protected persons adversely affected. To do this, the agency must “take into account the correct population base and its racial makeup.” Darensburg, 636 F.3d at 520. This step in a statistical analysis of disparate impact, therefore, is to identify the base population from which to draw comparative evidence, because the challenged policy must be shown to have a discriminatory effect within the population or area it affects. See, e.g., Hallmark Developers, Inc. v. Fulton Cty., 466 F.3d 1276, 1286 (11th Cir. 2006). In other words, the legally relevant “population base” for a statistical measure of adverse disparate impact is all persons the policy or practice affects or who could possibly be affected by some change in (or the elimination of) the policy or practice. Normally, this means “persons subject to the challenged … practice.” Carpenter v. Boeing Co. , 456 F.3d 1183, 1196 (10th Cir. 2006). As stated in a Fair Housing Act case, Housing Investors, Inc. v. City of Clanton , 68 F. Supp. 2d 1287, 1299 (M.D. Ala. 1999), “the starting point is always the subset of the population that is affected by the disputed decision.”
As these cases show, because the ultimate question is whether the policy has a discriminatory effect within the population it affects, statistical evidence ideally should be based on comparison groups that include, but do not extend beyond, “the total group to which the policy was applied.” Betsey v. Turtle Creek Assoc. , 736 F.2d 983, 987 (4th Cir. 1984). Part (a) of this section, below, discusses comparison groups that include the total group to which the policy applies.
Of course, the ideal evidence, i.e., statistical proof that covers the relevant population, is not always available. Investigating agencies may find that additional issues arise in attempting to analyze disparate impact within the affected population or area using statistical evidence that is not always a perfect fit. As discussed in part (b), sometimes the sources of available data may describe only a population smaller or larger than the population actually subject to the challenged policy. Other times, comparison groups are simply unavailable because the disparate effects of the policy or practice cannot be isolated or the policy or practice has a uniform, or near uniform, adverse effect on a predominantly minority population or area. Section (b) provides some additional guidance on methods that may be available to address these complications.
(a) Comparator Groups that Include the Total Group to which the Policy was Applied
Determining the population to which the challenged policy is applied or area the policy actually affected can present a challenging, fact-intensive element of proof. In certain types of cases involving whole areas, like cities, counties, or states, the investigating agency may use general population data where everyone in that population may be affected. Investigating agencies may find this method more efficient than other options because general population data are often readily available at little or no cost through existing sources. For example, in Angelita C. v. California Department of Pesticides Regulation , No. 16R–99–R9, an EPA administrative case, complainants alleged that the use of a particular pesticide caused adverse health risks borne disproportionately by Latino school children. EPA correctly measured disparity within the population base of all students enrolled in California public schools because all school children “could potentially have been affected” by the use of that pesticide, depending on proximity of the school to the farm using the pesticide and meteorological conditions. EPA Office of Civil Rights, Investigative Report for Title VI Admin. Complaint File No. 16R–99–R9 at 32 (Aug. 25, 2011). [15]
Similarly, in a Fair Housing Act (FHA) disparate impact claim that challenged the effect of a generally applicable zoning ordinance or other local law, the court determined that the legally relevant population base was everyone who lived in the city where the allegedly discriminatory fire code applied. Tsombanidis v. W. Haven Fire Dep’t, 352 F.3d 565, 577 (2d Cir. 2003) (fire code used to bar group home for recovering alcoholics and drug addicts violated FHA and Title II of the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990, 42 U.S.C. §§ 12131–12165).
By contrast, in an FHA disparate impact claim that challenge a more focused policy or practice, the court rejected an attempt to use generalized population data. Betsey, 736 F.2d at 987–88. In Betsey, plaintiffs challenged an apartment complex’s institution of a no-children policy in one of its buildings, resulting in the evictions of many African-American residents. Id. at 985–86. The court held that the only relevant question was the policy’s effect on African-American tenants of that building; it was irrelevant that the policy had little disparate impact on African-American residents community-wide, because the policy did not apply so broadly. Id . at 987–88. Because the percentage of minority residents receiving eviction notices was far higher than that of non- minority residents receiving eviction notices, a showing of disparate impact was “self-evident.” Id. at 988.
The history of Title VII disparate impact claims also suggests that agencies must be very cautious in the use of jurisdiction-wide population statistics. While courts sometimes allowed plaintiffs in early cases to use the population of the surrounding area as the population base for determining whether an employer’s hiring practices had an adverse disparate impact on a protected class, see, e.g., Griggs, 401 U.S. at 430, it is now clear that the legally relevant population base is the actual applicant pool or qualified applicant pool. See, e.g., Paige v. California , 291 F.3d 1141, 1145 (9th Cir. 2002) (“In evaluating the impact of a particular process, we must compare the group that ‘enters’ the process with the group that emerges from it.”); Stout v. Potter , 276 F.3d 1118, 1123 (9th Cir. 2002) (“Generally, the appropriate population is the applicant pool or relevant labor market from which the positions at issue are filled.”) (citing Wards Cove Packing Co. , 490 U.S. at 650–51); Hazelwood Sch. Dist. v. United States, 433 U.S. 299, 308 (1977)).
Although Title VI matters are less frequently the subject of litigation than housing or employment cases, the test for determining the relevant population base from which to measure disparity in a Title VI case is the same. In Larry P. v. Riles, 793 F.2d 969 (9th Cir. 1984), for example, plaintiffs claimed that California used an IQ test to place children in non-academic track classes, resulting in an adverse impact on black children. The relevant population base was all school children who took the test. The court concluded that plaintiffs made out a prima facie case by showing that “black children as a whole scored ten points lower than white children on the tests, and that the percentage of black children in [non-academic-track] classes was much higher than for whites.” Id. at 982–83. Similarly, in Bryan v. Koch , 627 F.2d 612, 617 (2d Cir. 1980), where plaintiffs alleged that closing a city hospital serving a 98% minority population violated Title VI, the court determined that the relevant population base was “the patients served by the City’s municipal hospital system.” Id. Because the general population was 66% minority-significantly less than the 98% minority population served by the hospital slated for closing-sufficient racial disparity was established. Id.
AGENCY PRACTICE TIP
When, and only when, an agency can reasonably conclude that everyone in the jurisdiction is potentially affected, investigating agencies can rely on Title VII and FHA disparate impact cases to support using an entire jurisdiction as the relevant population base.
(b) Comparator evidence that is not coextensive with the population subject to the policy
While the better practice is to analyze the population actually subject to the challenged policy, courts have recognized that evidence may not be available to measure this directly. For example, if the claim includes an allegation that a particular policy or practice created a pool where a particular group’s numbers were low precisely because the policy discouraged that group from applying, then plaintiffs must use some means to accurately estimate what the population makeup would have been without that policy or practice. See, e.g., Dothard v. Rawlinson, 433 U.S. 321, 330 (1977) (noting that “[t]here is no requirement … that a statistical showing of disproportionate impact must always be based on analysis of the characteristics of actual applicants” in part because “[t]he application process might itself not adequately reflect the actual potential applicant pool, since otherwise qualified people might be discouraged from applying because of a self-recognized inability to meet the very standards challenged as being discriminatory”).
In some cases, agencies facing this limitation may use evidentiary samples that are not coextensive with the population subject to the policy as long as those samples are representative of that population. For example, job applicants who actually take an allegedly discriminatory test, and whose pass rates can be compared for racially disparate results, represent only a portion of the affected population, which includes all potential job applicants. See Elaine W. Shoben, Differential Pass-Fail Rates in Employment Testing: Statistical Proof Under Title VII, 91 Harv. L. Rev. 793, 794 (1978); Frazier v. Consol. Rail Corp ., 851 F.2d 1447, 1452 (D.C. Cir. 1988). That does not mean pass rates are without evidentiary value; it just means decision-makers must attempt to use that information to determine the discriminatory effect the test would have on individuals in the relevant geographic area who could have taken the test.
Courts, in fact, routinely reject evidence when the sample is not sufficiently probative. In Smith v. Xerox Corp . 196 F.3d 358 (2d Cir. 1999) (overruled on other grounds by Meacham v. Knolls Atomic Lab., 461 F.3d 134 (2d Cir. 2006)), for example, the court considered the process each Xerox work unit used when deciding which workers to lay off. Plaintiffs, alleging age discrimination company-wide, presented statistics showing the relative retention rates of older and younger workers only within their particular units. The court found this evidence inadequate, as it demonstrated only a varying level of disparity in those particular units and not that such an effect pertained to the company as a whole. Id. at 369–70. It concluded that “isolating a few work-groups and analyzing the effect of [the company’s policy] on each work-group is misleading at best” when the challenge is to the effect the policy causes company-wide. Id. at 370. Similarly, in Darensburg, plaintiffs attempted to challenge the impact of a portion of a transit system’s expansion policy by presenting evidence regarding the impact on a particular group of minority bus riders [16] The court concluded that the expansion policy affected all transit users and held that it must therefore analyze the impact of the plan on all minority transit users, not just minority bus riders. 636 F.3d at 520.
Other times, the available evidence is of a pool that is broader than those affected by the challenged policy. This evidence, too, can be useful as long as that broader pool is representative of the affected population. See, e.g., EEOC v. Joint Apprenticeship Comm. of Joint Indus. Bd. of Elec. Indus., 186 F.3d 110, 119 (2d Cir. 1999) (using general population data, in addition to other statistical methods, to estimate the qualified labor pool). For example, in a challenge to a company’s requirement that job applicants have high school diplomas or pass standardized tests, the Supreme Court accepted evidence of racial disparity in high school graduation rates statewide and in standardized test pass rates nationally. Griggs, 401 U.S. at 430 n.6. Similarly, in Dothard, 433 U.S. at 330, the Court accepted nationwide evidence of how many women met challenged height and weight requirements. In both cases, there was no reason to think that local conditions varied significantly from the broader ones.
In contrast, courts may reject evidence of racial disparity gleaned from broad statistics where there is a reason to question whether those statistics are representative of the affected population. For example, in Johnson v. Uncle Ben’s, Inc., 965 F.2d 1363, 1369 (5th Cir. 1992), the court rejected national statistics about education levels by race in a challenge to a company’s promotion policy because those statistics were not necessarily representative of workers already working for the company and seeking promotion. Similarly, in Fletcher v. Berkowitz Oliver Williams Shaw & Eisenbrandt, 537 F. Supp. 2d 1028, 1030 (W.D. Mo. 2008), in a challenge to an employer’s consideration of plaintiff’s prior sexual assault conviction, the court rejected as immaterial the argument that African Americans were overrepresented in the larger pool of people with felony convictions. The court stated that the general felony data said nothing about the representation of African Americans among those with sexual assault convictions, which was the reason the employer terminated this employee.
AGENCY PRACTICE TIP
Use of general population data can simplify an agency’s disparate impact analysis where local demographic data about the population actually subjected to a challenged policy is simply not available. Part D discusses the critical role of agency data collection authority to meaningful disparate impact analyses. But agencies should use generalized data with caution: some showing must be made that evidence drawn from a national pool, or from another sample that is not coextensive with the population affected, is sufficiently and closely representative of the affected population.
iv. Determining the Significance of the Disparity
Once the relevant adversely affected and comparator populations are determined, investigating agencies must determine whether the disparity is large enough to matter, i.e., is it sufficiently significant to establish a legal violation. The magnitude of the disparity necessary may be difficult to define in some cases, but guidance can be drawn both from judicial consideration of this question and from federal agency guidelines. In many cases, courts have shied away from drawing clear lines. See Clady v. Cty. of Los Angeles, 770 F.2d 1421, 1428–29 (9th Cir. 1985); accord Smith v. Xerox Corp., 196 F.3d at 366 (“[T]he substantiality of a disparity is judged on a case-by-case basis.”); Groves, 776 F. Supp. at 1526 (“There is no rigid mathematical threshold that must be met to demonstrate a sufficiently adverse impact.”). Some disparities are so self- evidently significant, however, that courts have seen no need to explain their reasoning beyond presentation of the statistical evidence. See, e.g., Betsey, 736 F.2d at 988 (building policy resulted in 54.3% of non-white tenant households receiving eviction notices, compared with 14.1% of white households); Charleston Hous. Auth. v. U.S. Dep’t of Agric., 419 F.3d 729, 734 (8th Cir. 2005) (disparate impact caused by planned demolition of public housing units where 46 of the 47 families occupying units were African-American).
Conversely, courts are comfortable rejecting particularly small disparities, or those based on very small sample sizes, without explaining the mathematical basis for their conclusions. For example, one court found insufficient evidence of disparate impact based on sex where women were six of the thirty-eight applicants and received two of the fifteen interviews. As the court observed, if just one more female applicant had received an interview, women actually would have had a higher percentage of interviews granted. Stout, 276 F.3d at 1123 & n.2. Another court found insufficient disparate impact where “the pass rate for black applicants … was 93% that of white applicants,” without opining on what might be a sufficient showing. Moore v. Southwestern Bell Tele. Co., 593 F.2d 607, 608 (5th Cir. 1979) (per curiam). Importantly, plaintiffs have succeeded in establishing disparate impact, even with very small sample sizes, in cases where statistics were not necessary because the disparate effect was obvious or predictable. This approach is discussed above in subsection ii.
Enforcement agencies have developed guidelines to help identify sufficiently significant disparities in frequently recurring contexts. In employment discrimination cases, where the members of one race or other protected class are selected at four-fifths (or less) the rate of another (80% or less), the EEOC, DOJ, and the Department of Labor have adopted this formula for use in identifying evidence of disparate impact. [17] Some courts have adopted this four-fifths cutoff as a rule of thumb when determining whether the amount of differential impact is sufficient. See, e.g., Clady, 770 F.2d at 1429 (finding that written exam for employment adversely affected Hispanics because they passed at less than four-fifths the rate of white applicants).
However, not every type of disparity lends itself to the use of the four-fifths rule, even with respect to employment decisions. Federal guidelines in employment cases clarify that the four- fifths (80%) rule is not dispositive and smaller differences in selection rates may nevertheless constitute adverse impact. 28 C.F.R. § 50.14(4)(D). Some courts have found a prima facie case where the disparity fell just short of four-fifths but the causation analysis (discussed below) was statistically significant (meaning the disparity is less likely due to chance) and, in the court’s view, of practical import. See, e.g., Groves, 776 F. Supp. at 1527–28 (disparate impact established where defendant’s evidence revealed black candidates met testing requirement at 82.3% the rate of white candidates, slightly above the 80% mark, but the causation analysis was “overwhelming[ly] statistically significant, showing that “the test itself, and not merely random sampling, has caused the disproportionate exclusion of blacks”); Hill v. Metro. Atlanta Rapid Transit Auth., 591 F. Supp. 125, 129 (N.D. Ga. 1984) (acknowledging that disparate impact could still be established where minorities’ selection rate was 81.55% that of white candidates), rev’d in part on other grounds, 841 F.2d 1533 (11th Cir. 1988).
As noted above, in addition to the four-fifths (80%) rule, courts have considered statistical significance—the difference between the expected and observed rates in terms of standard deviations—with a difference of two or three standard deviations to be statistically significant (Hazelwood test). Similarly, the “Shoben formula” recognizes a “Z-value” measuring the difference in the groups’ success rates greater than 1.96 standard deviations to be statistically significant. Groves, 776 F. Supp. at 1526–28, citing Richardson v. Lamar Cty. Bd. of Educ., 729 F. Supp. 806, 816 (M.D. Ala. 1989).
Some agencies have suggested guidelines for disparity that may be considered significant. Following the focus in Groves on overwhelming statistical significance (part of the causation analysis), the Department of Education’s Office for Civil Rights has issued guidance in the context of high stakes testing indicating that, in general, a test has a disproportionate adverse impact if a statistical analysis shows a significant difference from the expected random distribution of test scores and pointing out that different courts have used different methods for determining disparate impact. U.S. Department of Education, Office of Civil Rights, The Use of Tests as Part of High-Stakes Decision-Making for Students: A Resource Guide for Educators and Policy-Makers (December 2000). [18] See also EPA Investigation Guidance, 65 Fed. Reg. at 39,682 (“[W]here credible measures of [disparity] are at least a factor of 2 times higher in the affected population, OCR would generally expect to find disparate impact under Title VI ….”).
Some agencies may use other methods of evaluating disparity. Some disparity measures, for example, may consider differences in the magnitude of adversity/harm (e.g., level of exposure or risk). Agency guidelines may evaluate both the demographic disparity and the differences in the magnitude of the impacts. For example, EPA’s Title VI investigations guidance established a sliding scale that takes into account the degree of demographic disparity and the differences of degree in the health impact measure (e.g., rates of cancer risks). Id. (“[W]here a large disparity exists in terms of impact and a relatively slight disparity exists with regard to demographics (or vice versa), EPA will ordinarily attempt to balance these factors, taking into account the particular circumstances of the case.”). While this does not provide a uniform standard for determining whether any individual matter has a discriminatory effect, it makes clear that the agency regards these two factors- degree of health impact and degree of demographic disparity-as important components of the analysis.
The Federal Transit Administration’s approach to disparate impact analysis, like EPA’s, recognizes the need for flexibility in determining whether there is disparity and considers differences in degree related to adversity/harm. Certain recipients are required to adopt a disparate impact policy that establishes “a threshold for determining when adverse effects of service changes are borne disproportionately by minority populations.” FTA Title VI Circular at Chap. IV–13.[19] The threshold should define “statistically significant disparity and may be presented as a statistical percentage of impacts borne by minority populations compared to impacts borne by non- minority populations.” Id.
d. Establishing Causation
The final element of adverse disparate impact is causation. Even if the evidence establishes an adverse effect that is borne disproportionately by members of a protected group, this question remains: did the recipient actually cause that effect? As the court held in Flores v. Arizona, 48 F. Supp. 2d 937, 952 (D. Ariz. 1999), “[p]laintiff’s duty to show that the practice has disproportionate effect requires plaintiff to demonstrate a causal link between the practice and the disparate impact identified.” To establish a violation of its disparate impact provision, an investigating agency must determine that the impact is causally linked to a recipient’s policy or practice. See Elston v. Talladega Cty. Bd. of Educ., 997 F.2d 1394, 1415 (11th Cir. 1993) (citations omitted) (plaintiff cannot make out a prima facie disparate impact claim if the evidence tends to show that even had the defendant not engaged in the challenged practice, the same disparate impact would nonetheless have existed).
Causation is frequently shown with statistics. To establish causation, the investigating agency may identify “statistical evidence of a kind and degree sufficient to show that the practice in question has caused the exclusion of [a particular group] because of their membership in a protected group.” Rose v. Wells Fargo & Co., 902 F.2d 1417, 1424 (9th Cir. 1990) (emphasis added) (citing Watson Watson v. Fort Worth Bank & Trust, 487 U.S. 977, 994 (1988). The statistical disparities must be sufficiently significant that they “raise … an inference of causation.” Id. As should already be clear, this method of proving causation is linked to the statistical proof of disparity discussed above; i.e., the same comparative population evidence is typically used to prove both causation and disparity. While the previous section looked at whether the magnitude of the disparity is large enough to matter, this analysis allows agencies to be sufficiently certain (at the specified statistical level) that the disparity is not caused by chance. In other words, is the difference statistically significant?
As discussed above, statisticians have their own established definitions of statistical significance that federal agencies can readily import in their analyses. See, e.g., 28 C.F.R. § 50.14(4)(D). Federal regulations generally define statistical significance, consistent with the term’s typical use in social sciences and other statistical inquiry, as a demonstration that the disparity has “a probability of no more than one (1) in twenty (20) to have occurred by chance.” Id. § 50.14(14)(B)(5); see also Castaneda v. Partida, 430 U.S. 482, 496 n.17 (1977); Alexander v. Louisiana, 405 U.S. 625, 630 & n.9 (1972); Watson, 487 U.S. at 995 (O’Connor, J., plurality opinion) (“statistical disparities must be sufficiently substantial that they raise … an inference of causation”). However, as discussed above there are multiple tests for statistical significance that allow for different confidence intervals (e.g. the Hazelwood test allows for statistical significance at 2-3 standard deviations from the expected rates and the Shoben formula allows 1.96 standard deviations). See Groves, 776 F. Supp. at 1526–28.
Regardless of the statistical significance measure used, the Supreme Court has emphasized the importance of “a robust causality requirement” in ensuring entities are not “held liable for racial disparities they did not create.” Inclusive Communities, 135 S. Ct. at 2523 (citing Wards Cove, 490 U.S. at 653). Investigating agencies must carefully evaluate the causal connection between the challenged policy and any adverse disparate impacts identified. Yet, it is important to remember that the causation element is not a fault-based inquiry; the proper analysis is not about whether there are actual differences among applicants or beneficiaries of different races or why those differences exist. Rather, the sole question at this phase of the case should be whether the recipient’s policy in fact affects people of different races disproportionately. Causation is established where the evidence establishes that the recipient’s policy or practice operates in this manner; there is no need for understanding why the policy results in the disparity at this step of the inquiry.
Other types of Title VI cases may involve a different type of causation analysis—one that explores the concrete proof connecting the recipient’s practice to the alleged harms. For example, environmental justice cases often involve allegations that a recipient’s action or inaction causes harm or that the recipient’s permitting of a third party facility causes the harm. In these cases, establishing causation may involve scientific or other quantifiable proof that the challenged practice actually caused the alleged adverse impacts. This may involve proof connecting a specific facility to a specific adverse impact, such as harmful health effects, odor, noise, decrease in property values, etc. When such proof is not obtainable, the statistical tests discussed above will suffice.
For example, in complaint investigations alleging adverse impacts from the operation of recipient-permitted facilities, EPA has explained that the facts and circumstances of each complaint will determine whether a likely causal link exists. EPA recognizes a number of forms and types of evidence that could establish causation, including scientific proof of a direct link, prediction of potentially significant exposures and risks resulting from stressors created by the permitted activities or other sources, and other complex methodologies. EPA Investigations Guidance, 65 Fed. Reg. at 39,679. For an example of a causation analysis involving the risk of exposure to a pesticide, see EPA’s investigatory report in Angelita C. v. California Department of Pesticides Regulation, No. 16R–99–R9. EPA Office of Civil Rights, Investigative Report for Title VI Administrative Complaint File No. 16R–99–R9 at 32–33 (Aug. 25, 2011).[20]
e. Agency Approaches to Defining Adverse Disparate Impact
As mentioned previously, federal funding agencies responsible for Title VI enforcement sometimes engage in rulemaking, issue formal guidance documents, and informal guidance such as letters to inform recipients of the types of adverse disparate impact (discriminatory effects) they must try to avoid. In the following illustrative examples of agency approaches to defining adverse disparate impact in specific applications, agencies have identified specific impacts prohibited by Title VI; identified factors they will consider in making such determinations on a case by case basis; and required (or recommended) that their recipients establish formal definitions.
2. The Recipient's Substantial Legitimate Justification
If the evidence establishes a prima facie case of adverse disparate impact, as discussed in the preceding sections, courts then determine whether the recipient has articulated a “substantial legitimate justification” for the challenged policy or practice. Georgia State Conf. v. Georgia, 775 F.2d 1403, 1417 (11th Cir. 1985). The justification inquiry is an important and appropriate means of ensuring recipients have “leeway to state and explain the valid interests served by their policies.” Inclusive Communities, 135 S. Ct. at 2522.
AGENCY PRACTICE TIP
The sequential process that courts use, where a complainant offers prima facie evidence and the defendant offers a rebuttal or a “substantial legitimate justification” need not be how an agency conducts its investigation. Rather, an agency has discretion to gather and evaluate evidence of “substantial legitimate justification” as part of its initial investigation, or to make a preliminary finding and require recipients to articulate their defenses as a next step. For example, EPA Title VI guidance recognizes the “recipient may offer its justification following its receipt of the notice of complaint, or after a preliminary finding of non–compliance with Title VI or EPA’s implementing regulations.” EPA Draft Revised Investigations Guidance, 65 Fed. Reg. at 39,683.
In contrast to intentional discrimination cases, where recipients can offer legitimate non- discriminatory reasons for the challenged actions, a justification in a disparate impact case that merely dispels inferences of illegitimate intent is inadequate. “Substantial legitimate justification” in a disparate impact case is similar to the Title VII concept of “business necessity,” which requires an employer to show that the policy or practice in question is demonstrably related to a significant, legitimate employment goal. Griggs, 401 U.S. 433–36; Wards Cove, 490 U.S. at 659. After the plaintiff establishes a prima facie case of disparate impact, the defendant can attempt to show that the challenged practice “serves, in a significant way, the legitimate employment goals of the employer.” Id. Importantly, the concept of “business necessity” does not transfer exactly to the Title VI context because Title VI covers a broader scope of recipient practices. See Inclusive Communities, 135 S. Ct. at 2522–24 (recognizing the limitations on extension of the business necessity concept to Fair Housing Act cases).
Thus, while it is well-established that unjustified disparate impact violates agency Title VI regulations, the precise nature of the justification inquiry in Title VI cases is somewhat less clear in application. As discussed in more detail below, courts and agencies have articulated a number of different formulations to describe what constitutes a justification legally sufficient to permit an adverse disparate impact. In all of these formulations, this analysis requires a delicate balancing of recipients’ interests in implementing their policies with the substantial public interest in preventing discrimination. Because Title VI covers a vast array of federally funded programs, each with a different institutional mission, this highly fact-specific inquiry must be made carefully case by case.
Although determining a substantial legitimate justification is a fact-specific inquiry, Title VI case law and agency guidance set forth general requirements. For example, courts have required that the recipient show that the challenged policy was “necessary to meeting a goal that was legitimate, important, and integral to the [recipient’s] institutional mission” in order to establish a “substantial legitimate justification.” Elston, 997 F.2d at 1413 (emphasis added). Courts have evaluated whether the policy was “necessary” by requiring that the justification bear a “manifest demonstrable relationship” to the challenged policy. Georgia State Conf., 775 F.2d. at 1418 (11th Cir. 1985).
SUBSTANTIAL LEGITIMATE JUSTIFICATION
Was the challenged policy necessary to meeting a goal that was legitimate, important, and integral to the recipient’s institutional mission?
Does the justification bear a manifest demonstrable relationship to the challenged policy?
Agency guidelines or regulations implementing Title VI incorporate similar formulations. See, e.g., EPA Investigations Guidance, 65 Fed. Reg. at 39,654 (“Determining what constitutes an acceptable justification will necessarily be based on the facts of the case. Generally, the recipient would attempt to show that the challenged activity is reasonably necessary to meet a goal that is legitimate, important, and integral to the recipient’s institutional mission.”); Fair Housing Act Regulations, 24 C.F.R. § 100.500(b)(1), (c)(2) (under the second step of the disparate impact burden shifting analysis, the defendant must prove that the proposed action is “necessary to achieve one or more substantial, legitimate, nondiscriminatory interests” of the defendant).
As is clear, this inquiry is fact-specific; this section does not present an exhaustive list of factors, but rather some of the considerations that may guide an investigating agency's analysis.
AGENCY PRACTICE TIP
Agencies provide guidance concerning types of justifications they expect to consider when investigating particular case types. See, e.g., HUD Office of General Counsel Guidance on Application of the Fair Housing Act Standards to the Use of Criminal Records by Providers of Housing and Real Estate–Related Transactions (April 4, 2016), available at https://perma.cc/A49W- XJNC (resident safety and protecting property may be both substantial and legitimate, but housing providers must be able to prove that policies making housing decisions based on criminal history actually assist in protecting resident safety and/or property); EPA Draft Revised Investigations Guidance, 65 Fed. Reg. at 39,683 (explaining that when evaluating justifications for discriminatory environmental permitting decisions, EPA “expects to consider provision of public health or environmental benefits (e.g., waste water treatment plant) to the affected population from the permitting action to be an acceptable justification because such benefits are generally legitimate, important, and integral to the recipient’s mission”); DOJ Language Guidance Letter to State Courts, (Aug. 16, 2010), available at http://www.lep.gov/final_courts_ltr_081610.pdf (explaining how cost justifications will be evaluated in the language access context).
Federal funding agencies are uniquely qualified to provide such guidance because of their expert knowledge of their funded programs. Courts normally defer to agency guidance in evaluating specific types of disparate impact. See, e.g., S. Camden Citizens in Action, 145 F. Supp. 2d 446, 496 (D.N.J. 2001) (“In the absence of guiding legal precedent on the question of what constitutes a ‘substantial legitimate justification’ or a ‘legitimate nondiscriminatory reason’ in the context of this case, I shall look to EPA regulations and practice.”). As in all aspects of Title VI investigation, agencies should consider not only the recipient’s perspective, but also the views of the affected community in assessing whether benefits to the community outweigh the policy’s disproportionate adverse effects. See, e.g., EPA Investigations Guidance, 65 Fed. Reg. at 39,683.
a. Is the Proffered Justification legitimate, integral to the recipient's institutional mission,
and important?
Agencies should first inquire whether the recipient offers a justification that is legitimate, integral to the recipient’s institutional mission, and important. Elston, 997 F.2d at 1413.
i. Legitimate
Recipients frequently articulate rationales that appear to be legitimate on their face. These rationales can be objective: for example, showing that the recipient considered multiple alternatives and selected the least damaging/most beneficial path. See, e.g., New York City Envtl. Justice All. v. Giuliani, 214 F.3d 65, 72 (2d Cir. 2000); see also Inclusive Communities, 135 S. Ct. at 2523 (noting that “[z]oning officials … must often make decisions based on a mix of factors, both objective (such as cost and traffic patterns) and, at least to some extent, subjective (such as preserving historic architecture)” and that “these factors contribute to a community’s quality of life and are legitimate concerns for housing authorities.”)
Where, however, a federally funded entity insists on implementing a policy despite its adverse disparate impacts, the investigating agency must scrutinize the recipient’s rationale to determine whether the evidence adequately supports it. A violation is established if the investigating agency finds that the evidence does not support the entity’s justification, and therefore is not legitimate. See Elston, 997 F. 2d at 1407. Federal Transit Administration guidance explains this critical point: “[I]f evidence undermines the legitimacy of the [recipient’s] asserted justification-that is, that the justification is not supported by demonstrable evidence-the disparate effects will violate Title VI, as the lack of factual support will indicate that there is not a substantial legitimate justification for the disparate effects.” FTA Title VI Circular, at ch. IV–16.
Court decisions show that agencies should be particularly skeptical of “subjective rationales” and should thoroughly investigate and analyze the facts to determine whether these rationales are supported by sufficient evidence. See, e.g., Sandoval v. Hagan, 197 F.3d 484, 490–91 (11th Cir. 1999), rev’d on other grounds sub nom. Alexander v. Sandoval, 532 U.S. 275 (2001). In Sandoval, the Eleventh Circuit affirmed the district court’s determination that none of the facts supported the recipient state agency’s rationale for limiting driver’s license examinations only to people who spoke English. Id. The state agency offered several justifications for the English- only rule: highway safety concerns, exam administration difficulties, exam integrity, and budgetary constraints. Id. The district court found that the recipient had produced no evidence at trial that non-English speakers posed a greater driving safety risk than English speakers; the recipient had undermined its own safety argument by recognizing valid licenses from non- English speakers of other locales; making test accommodations for illiterate, deaf, and disabled drivers; and having previously offered the examination in fourteen languages without administrative difficulty. The court further noted that cost had not been a real factor in making the decision to administer the examination only in English and that the recipient could afford the costs of language assistance in light of its $50 million dollar budget. Id. Affirming the district court, the Eleventh Circuit ruled that the state agency’s rationales constituted a pretext for the policy despite its established disparate impact on national origin minorities. Id.
The justification analysis used in Fair Housing Act disparate impact cases can also provide guidance for Title VI investigating agencies. The justification “must be supported by evidence and may not be hypothetical or speculative.” 24 C.F.R. §§ 100.500(c)(2), 100.500(b)(2); see, e.g., Gashi v. Grubb & Ellis Prop. Mgmt. Servs., Inc., 801 F. Supp. 2d 12, 16 (D. Conn. 2011) (explaining that where the “defendant presents objective evidence to support his assertions, the court is less wary of subjective explanations”) (citing Soules v. HUD, 967 F.2d 817, 822 (2d Cir. 1992)). The Gashi court found that the evidence did not support a housing authority’s justifications for its discriminatory occupancy limitation. The defendant argued that the local fire code mandated the challenged occupancy requirements and that “building infrastructure concerns” necessitated the policy. The court concluded, however, that the fire code defendants cited actually was not binding because it represented only national guidelines, and the defendants had no documentation to support their vague assertions regarding infrastructure concerns. Id. at 17–18. See also Charleston Housing Authority v. U.S. Dep’t of Agriculture, 419 F.3d 729, 741 (8th Cir. 2005) (rejecting as unsupported by the evidence defendant housing authority’s claim that demolition of public housing units occupied almost entirely by African Americans was justified by a desire for low-income housing density reduction, need to eliminate a housing design that contributed to the concentration of crime and drug use, and lack of funding for necessary improvements).
It is important for investigating agencies to evaluate the veracity of any cost-based justifications the recipient puts forward. A monetary justification for a policy or practice (or lack thereof) will often fail because of a lack of evidence. See, e.g., Sandoval v. Hagan, 7 F. Supp. 2d 1234, 1312 (M.D. Ala. 1998) (finding defendant’s cost argument unsupported by the evidence because translation services at issue could be obtained by alternative cost-effective means); aff’d, 197 F.3d 484 (11th Cir. 1999) rev’d sub nom. Alexander v. Sandoval, 532 U.S. 275 (2001); Charleston Hous. Auth., 419 F.3d at 742; Department of Justice, Civil Rights Division, Complaint No. 171–54M–8, Letter to N.C. Courts from Assistant Attorney General (March 8, 2012) at 15–16 (rejecting the recipient’s cost justification in part because it had access to new funds, none of which increased language access services in the courts; the cost of providing services was a small fraction of its operating budget; and it prevented courts from providing interpreters even when there would be no financial cost to do so); [24] but see NAACP v. Wilmington Med. Ctr., Inc., 491 F. Supp. 290, 342 (1980) (crediting defendant’s evidence that the costs associated with avoiding relocation of medical center from an urban to suburban location would require borrowing well beyond defendant’s budget).
Finally, a recipient cannot simply contend that it followed other applicable rules governing site selection or permit approvals to establish a legitimate justification. See S. Camden Citizens in Action, 145 F. Supp. 2d at 496 (rejecting defendant’s argument that the challenged facility’s compliance with the National Ambient Air Quality Standard constitutes a substantial, legitimate justification for its permitting decision). Mere compliance with rules unrelated to civil rights prohibitions does not legitimize a justification that would otherwise be insufficient under Title VI to justify adverse disparate impacts. In most instances, determining compliance with other rules or requirements involves reasoning based exclusively on those rules and “does not include considerations required by Title VI.” Id. at 496.
ii. Integral
Federal funding agencies should also consider the type of recipient in evaluating the adequacy of the recipient’s proffered justification. Different types of institutions obviously have different interests. What is central to the mission of one type of recipient may be merely tangential to, or even contrary to, the central mission of another. See Wilmington Med. Ctr., 491 F. Supp. at 316 (acknowledging that Title VI could be applied to a wide range of entities and to an equally diverse range of decisions and, therefore, the nature of the justification required might vary from case to case). For instance, crime reduction may be part of a law enforcement agency’s integral institutional mission, but may be only minimally or even unrelated to the mission of other types of public entities .
iii. Important
The investigating agency’s evaluation of the importance of a recipient’s stated justification involves weighing the reason for implementing the challenged policy or practice against the harm it causes. See NAACP v Med. Ctr., Inc., 657 F.2d 1322, 1350 (3d Cir. 1981) (en banc) (“The content of the rebuttal or justification evidence cannot be determined in the abstract. It must be related to the precise impacts suggested by the plaintiffs’ evidence.”); see also Gashi, 801 F. Supp. 2d at 16 (citing Huntington Branch, NAACP v. Town of Huntington, 844 F.2d 929, 937 (2d Cir. 1988), aff’d, 488 U.S. 15 (1988) (“After the defendant presents a legitimate justification, the court must weigh the defendant’s justification against the degree of adverse effect shown by the plaintiff.”). Courts have also recognized that the degree of adverse impact that a challenged policy or practice causes can affect the sufficiency of the recipient’s justification. See, e.g., Clady v. Cty. of Los Angeles, 770 F.2d 1421, 1432 (9th Cir. 1985) (“As a general principle, the greater the test’s adverse impact, the higher the correlation which will be required.”). Generally, the more serious, significant, or widespread the adverse disparate impacts the challenged policy causes, the more difficult it will be for the recipient to establish a sufficient reason for implementing the policy.
b. Does the Challenged Policy Bear a Demonstrable Relationship to the Recipient's Stated Objective?
Even if the recipient points to a legitimate, important goal that is integral to its institutional mission, the discriminatory policy or practice must also bear a demonstrable relationship to that goal. Georgia State Conf., 775 F.2d. at 1418. If it does not, implementation of that policy or practice violates Title VI. Accordingly, the investigating agency must take a hard look at the connection between the challenged policy or practice and the recipient’s stated objective.
For example, in Leaders for Equality and Action in Dayton (LEAD) v. City of Beavercreek, the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) found that the City Council’s refusal to approve the construction of three bus stops caused unjustified disparate impact by denying minority residents public transit access to a shopping mall, a large medical center, jobs, and other essential services in Beavercreek. FHWA Office of Civil Rights, Letter from Associate Administrator for Civil Rights, DOT #2012–0020, at 15–16 (June 26, 2013). The City attempted to justify its decision by arguing, among other things, that installation of police call boxes and “state of the art” video surveillance would be necessary to protect the public and reduce the risk of crime at the stops. Id. at 12. FHWA acknowledged the City had a legitimate, important goal to ensure public safety, but found the record contained insufficient evidence to show the lack of call boxes and video surveillance at other comparable stops presented a public safety risk. Id. In other words, the City did not establish that the action taken bore a demonstrable relationship to the stated goal Moreover, the City offered no evidence that security and public safety were serious issues at comparable bus stops. Id. The FHWA concluded that the City failed to prove the necessary connection between the legitimate justification-public safety-and the challenged practice-the refusal to approve the construction of the three bus stops based on the asserted necessity to install police call boxes and video surveillance equipment.
c. Special Considerations: Site Selection or Facility Closures
Many Title VI cases involve challenges to site selection decisions, such as the locations selected for construction of highways or facilities that will have negative consequences for the surrounding community. Site selection cases can also involve challenges to the closure or relocation of desirable facilities, such as schools or hospitals. In such cases, courts have tended to merge the initial justification analysis with the final step of the disparate impact burden shifting framework, i.e., consideration of less discriminatory alternatives. That step is discussed in detail in Section 3 below. In determining the sufficiency of the recipient’s proffered reasons for the discriminatory siting or closure decision, courts consider not only whether the construction or closure was necessary to begin with but also whether the recipient can justify selection of the particular site over alternatives. See, e.g., Coalition of Concerned Citizens Against I-670 v. Damian, 608 F. Supp. 110, 127 (S.D. Ohio 1984). These cases show that consideration of less discriminatory alternatives is often linked to the “substantial legitimate justification” analysis, and agencies therefore should carefully consider recipients’ site selection process, including alternatives, when analyzing justification .
For example, in Damian, the court found that plaintiffs made a prima facie showing that recipients’ decision to build a new freeway would have a discriminatory effect because the freeway would travel through predominately minority neighborhoods, the majority of people displaced by the construction were racial minorities, and the disruptions and other negative impacts caused by the construction and eventual highway operation would fall disproportionately on those minority neighborhoods. Id. Nonetheless, the court further found that the recipients had met their burden of justifying the location of the interstate because the major alternative location would have had a substantially greater impact on minorities, and the recipients had selected the final freeway location “so as to minimize impacts upon minority neighborhoods,” avoiding most of the neighborhoods that were 90% racial minorities. Id. Critically, it was not enough to show that a new freeway was needed; rather, the court demanded that the recipient justify the specific location selected. See also Bryan, 627 F.2d at 617–18 (where public officials made a choice to close one of 17 municipal hospitals, it was “the choice of this particular hospital that must be justified”).
3. Less Discriminatory Alternative
If a substantial legitimate justification for the recipient’s discriminatory policy or practice is identified, the investigating agency must also determine whether there are alternative practices that may be comparably effective with less disparate impact. Title VI requires recipients to implement a “less discriminatory alternative” if it is feasible and meets their legitimate objectives. Elston, 997 F.2d at 1407, 1413; Georgia State Conf., 775 F.2d at 1417. This is a critical-and sometimes overlooked-stage of the investigation. Even if the recipient demonstrates a substantial legitimate justification, the challenged policy will nevertheless violate Title VI if the evidence establishes an alternative that meets this test.
Courts have been willing to thoroughly analyze alternatives, particularly where the recipient had considered and rejected them and thus the record was already developed. See, e.g., Damian, 608 F. Supp. 119–20 (conducting a thorough review of alternative sites for highway or other methods, such as light rail or public transportation). Where Title VI plaintiffs challenged broad institutional decisions, however, courts were sometimes reluctant to conduct a searching analysis of alternatives. See, e.g., Bryan, 627 F.2d at 619 (“We are skeptical of the capacity and appropriateness of courts to conduct such broad inquiries concerning alternative ways to carry out municipal functions. Once a court is drawn into such a complex inquiry, it will inevitably be assessing the wisdom of competing political and economic alternatives.”).
Federal funding agencies, on the other hand, are subject matter experts charged with specific Title VI enforcement duties. As a result, they are well-equipped to analyze alternatives thoroughly and they should evaluate carefully potential less discriminatory alternatives. This section discusses (a) who bears the responsibility to establish less discriminatory alternatives, (b) how evidence of less discriminatory alternatives must be specific, (c) how proposed alternatives must meet the recipient’s objectives, and (d) how less discriminatory alternatives may be of a different type than the challenged policy and can be achieved through mitigation measures.
a. Evidentiary Hearing
In disparate impact lawsuits, once the defendant establishes a substantial legitimate justification, the burden shifts back to the plaintiff to identify less discriminatory alternatives to the challenged policy or practice. Powell v. Ridge, 189 F.3d 387, 394 (3d Cir. 1999) (citing Georgia State Conf., 775 F.2d at 1417). In other words, the defendant is not obligated to prove that there were no such alternatives, and the burden of persuasion remains with the plaintiff to prove that there were. But cf. Damian, 608 F. Supp. at 128 (recognizing “there would be some question whether defendants were required by federal law to consider alternatives with less disparate impact” under Title VI).
In contrast, in agency Title VI administrative investigations, the evidentiary burden, as previously explained, rests with the investigating agency rather than with the complainant. EPA guidance explains this important distinction:
The investigation of Title VI administrative complaints by [EPA] does not involve an adversarial process, as in litigation, between the complainant and the recipient. Rather, it should be viewed as EPA investigating allegations that EPA financial assistance is being used improperly. Consequently, the complainants do not have the burden of proving that their allegations are true and are not obligated to offer less discriminatory alternatives. Instead, EPA has the responsibility to determine whether a violation exists and, where appropriate, to uncover less discriminatory alternatives. Nonetheless, EPA encourages complainants to provide whatever relevant information they may have.
EPA Investigations Guidance, 65 Fed. Reg. at 39,696 (emphasis added). Moreover, Title VI regulations require the recipient to provide the investigating agency with the data and information necessary to make this determination.
AGENCY PRACTICE TIP
Although agencies bear the burden of evaluating less discriminatory alternatives, agencies sometimes impose additional requirements on recipients to consider alternatives before taking action. These requirements can affect the legal framework by requiring recipients to develop the evidentiary record related to alternatives as a matter of course, before and regardless of whether an administrative complaint is even filed. Such requirements recognize that the recipient is in the best position to complete this task, having the best understanding of its goals, and far more ready access to the information necessary to identify alternatives and conduct a meaningful analysis. See Med. Ctr., 657 F.2d at 1355 (Gibbons, J., concurring and dissenting). Courts have recognized that agencies have authority to impose additional obligations. See, e.g., Damian, 608 F. Supp. at 128.
Many agencies have established additional requirements related to less discriminatory alternatives, under both Title VI and other authorities. For example, the Federal Transit Administration requires certain recipients to consider alternatives before implementing key decisions. A recipient’s failure to do so, and to gather sufficient data to establish it has selected the least discriminatory alternative, is a procedural violation of agency regulatory requirements, and may put the recipient at risk of a substantive violation as well. See FTA Title VI Circular, Chap IV–16. FTA explains the requirement to examine alternatives as follows:
Examining Alternatives. If the transit provider determines that a proposed service change will have a disparate impact, the transit provider shall analyze the alternatives … to determine whether alternatives exist that would serve the same legitimate objectives but with less of a disparate effect on the basis of race, color, or national origin. The existence of such an alternative method of accomplishing the transit provider’s substantial and legitimate interests demonstrates that the disparate effects can be avoided by adoption of the alternative methods without harming such interests.… At that point, the transit provider must revisit the service changes and make adjustments that will eliminate unnecessary disparate effects on populations defined by race, color, or national origin. Where disparate impacts are identified, the transit provider shall provide a meaningful opportunity for public comment on any proposed mitigation measures, including the less discriminatory alternatives that may be available. Id.
In some cases, a recipient is responsible for assisting in the development of a record of alternatives because it is involved in a project covered by the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA), 42 U.S.C. § 4321 et seq. This record may contain evidence that is also relevant and useful in determining compliance with Title VI. For example, recipients of funding from the Federal Highway Administration may be responsible for assisting in the development of the record of alternatives that the FHWA reviews in the NEPA process and related investigations.The FHWA follows the federal-government wide regulations implementing the procedural provisions of NEPA issued by the Council on Environmental Quality (CEQ) (40 C.F.R. parts 1500–1508) and has supplemented these procedures to take into account its programs. The CEQ regulations require a rigorous assessment of all reasonable alternatives. See 40 C.F.R. § 1502.14(a) (explaining that environmental impact statements under NEPA require the entity to “[r]igorously explore and objectively evaluate all reasonable alternatives”). The FHWA regulations require applicants to use early coordination to identify alternatives to the proposed action. See 23 C.F.R. §§ 771.119(b), 771.123(b)–(c), and 771.125(a)(1).
b. Specificity of Evidence of Alternatives and Relationships tot he Recipient's Mission
Investigating agencies should thoroughly review the evidence regarding potential alternatives. Plaintiffs in private litigation often fail to establish “less discriminatory alternatives” because their evidence of alternatives is not sufficiently specific. See, e.g., N.Y.C. Envtl. Justice All., 214 F.3d at 72 (in challenge to decision to sell community gardens in order to build new housing and foster urban renewal, plaintiffs suggested other vacant lots but presented no evidence that the defendant owned the lots or that they were suitable for housing); Damian, 608 F. Supp. at 128 (alternative “indirect” route for challenged highway was too speculative, there was no indication of specific route, economic cost, or social or environmental impacts); Lucero v. Detroit Pub. Sch., 160 F. Supp. 2d 767, 797 (E.D. Mich. 2001) (in challenge to school siting decision, plaintiffs argued that an alternate site would have been more appropriate, but failed to identify another viable site). Before finding a Title VI violation due to the availability of a “less discriminatory alternative,” agencies should determine that the evidence is sufficient and concrete, and not speculative.
Plaintiffs’ claims have also failed, notwithstanding an adverse impact, because plaintiffs could not identify an alternative that satisfies all of the defendants’ needs. See, e.g., Elston, 997 F.2d at 1413 (the only alternative identified did not provide sufficient land to accommodate defendants’ needs); Damian, 608 F. Supp. 120 (alternative sites for highway or other transportation options, such as light rail, public transportation, etc., were insufficient to meet the traffic demands served by added highway); African Am. Legal Def. Fund, Inc. v. New York State Dep’t of Educ., 8 F. Supp. 2d 330, 338 (S.D.N.Y. 1998) (in challenge to public school funding formula, plaintiff’s proposed alternative formula based on enrollment instead of attendance was legally insufficient because it failed to meet the objectives served by the existing formula); but see Meek v. Martinez, 724 F. Supp. 888, 906 (S.D. Fla. 1987) (in challenge to state formula for distributing funds under the Older Americans Act, plaintiff demonstrated that less discriminatory alternatives to the current formula were readily available and could be feasibly implemented).
In Goshen Road Environmental Action Team v. U.S. Dep’t of Agriculture, 176 F.3d 475, 1999 WL 187264 (4th Cir. 1999) (unpublished opinion), the court concluded that the alternatives plaintiffs presented for the siting of a wastewater treatment facility were unsuitable. Id. at *3. The recipient successfully argued that two alternative sites were poor choices because of the risk raw sewage could be released into a major river if the infrastructure in either location were to deteriorate. Other sites were unsuitable because of the poor quality of the soil. Of the two remaining potential sites, engineers selected the existing site because it required slightly less land, had better soil quality, its road frontage provided better access, and it was further from the town. Id. The court concluded the plaintiff had adduced “no scientific evidence of its own supporting its claim that other equally effective sites existed.” Id.
Similarly, in Darensburg v. Metropolitan Transportation Commission, 611 F. Supp. 2d. 994, 1060 (N.D. Cal. 2009), the district court held that plaintiffs did not show that the alternatives proposed would be “equally effective while causing less racial disparity.” In this challenge to a metropolitan planning organization’s complex scheme for allocating funding to various transit projects, plaintiff proposed a number of alternative funding allocation methods. The court took each proposal in turn, holding that plaintiffs failed to adduce sufficient evidence of their plans’ effectiveness. Id. at 1060–61. For instance, plaintiffs’ expert argued the recipient could first use federal funds for operations because it cannot collect interest on those funds, then use the remaining funds, which can earn interest, to pay for longer term projects. The court rejected this alternative because the plaintiff failed to show that the amount of interest that could be earned would be large enough to meet the recipient’s needs. Id. at 1060.
Importantly, alternatives need not be merely substitutes of the same type as the challenged practice, but may include practices or policies of a different manner or that include other actions by the defendant that ameliorate the disparate impact. See id. at 998–1000, 1060–61. For example, in Medical Center, plaintiffs challenged the recipient’s intention to close some city hospitals and build the primary medical facility in the suburbs, farther away from a predominantly minority community. Med. Ctr., 657 F.2d at 1325. Assuming a discriminatory effect resulted from the new location, the court upheld the action because the recipient considered and rejected various alternatives for legitimate reasons, noting that the alternative locations would not meet the recipient’s needs. The court also noted that the recipient had agreed to provide a shuttle service between the several hospitals for patients, visitors, and employees to lessen any hardship on people who needed to use the suburban facility. Id. at 1331–32, 1337.
Similarly, in the context of environmental permitting complaints, the use of “practical mitigation measures associated with the permitting action could be considered as less discriminatory alternatives, including, in some cases, modifying permit conditions to lessen or eliminate the demonstrated adverse disparate impact.” EPA Investigations Guidance, 65 Fed. Reg. at 39,683.
AGENCY PRACTICE TIP
These cases and guidelines show that “less discriminatory alternatives” may take the form of mitigation measures to be applied to the original challenged practice. Accordingly, investigating agencies should ensure that they consider not only alternative policies and practices when evaluating “less discriminatory alternatives,” but also the measures the recipient could implement in order to lessen the harm that the challenged practice causes. Informal resolution efforts often involve identification of mitigation efforts which, if applied, would result in compliance with Title VI through implementation of a less discriminatory alternative.
D. Agency Data Collection Authority and Measuring Disparate Impact
In many disparate impact cases, particularly those in which federal guidelines have not already established the types of impacts that are per se unlawful, demographic data will be important to the investigating agency’s analysis. See Darensburg, 636 F.3d at 522 (attributing plaintiffs’ loss to the lack of precise data necessary to determine the extent to which a project harmed minorities to a greater extent than regional-level statistics may have suggested).
Title VI regulations provide agencies with a clear mandate to collect the data necessary to ensure compliance with their Title VI disparate impact regulations. The Department of Justice Title VI coordination regulation states that “[e]xcept as determined to be inappropriate … federal agencies … shall in regard to each assisted program provide for the collection of data and information from applicants for and recipients of federal assistance sufficient to permit effective enforcement of Title VI.” 28 C.F.R. § 42.406(a). The coordination regulation then gives various examples of the types of data that agencies generally should require recipients to submit, including the racial and ethnic composition of the eligible population, the racial and ethnic impact of the location of facilities connected with the program, and any relocation involved in the program. Id. § 42.406(b). The coordination regulation also contemplates that agencies will collect “demographic maps, [and] the racial composition of affected neighborhoods or census data” where they are necessary to understand the considerations above, but “only to the extent that it is readily available or can be compiled with reasonable effort.” Id. § 42.406(c).
Consistent with these provisions, all agency Title VI implementing regulations specifically require that recipients collect and provide access to information that is necessary to determine compliance. [25] The applicable provision typically appears under the heading “compliance reports,” and mandates the following:
Each recipient shall keep such records and submit to the responsible Department official or his designee timely, complete, and accurate compliance reports at such times, and in such form and containing such information, as the responsible Department official or his designee may determine to be necessary to … ascertain whether the recipient has complied or is complying with this subpart.
See, e.g., id. § 42.106(b) (DOJ). This provision also requires the primary recipient to obtain from its subrecipients, and have available for agency review, such compliance reports “as may be necessary to enable the primary recipient to carry out its obligations.” Id.
These regulations permit agencies to exercise broad discretion in determining what sources of information “may be pertinent” to ascertain compliance with Title VI. Although rarely a litigated issue because the vast majority of recipients cooperate with agency data requests, in United States v. El Camino Community College District, 600 F.2d 1258, 1260 (9th Cir. 1979), the Ninth Circuit held that “[i]n exercising its investigatory powers” under Title VI, a federal agency “must have substantial latitude in scrutinizing policies and practices of the institution” for possible discrimination.
Moreover, these provisions are not limited to evidence gathered during a formal complaint investigation or compliance review but also allow for agency data collection during monitoring efforts. That is, agencies need not suspect discrimination in order to collect relevant demographic data but may do so to monitor or evaluate compliance. Courts have recognized that routine monitoring is a form of enforcement, Gillis v. U.S. Dep’t of Health and Human Servs., 759 F.2d 565, 575 (6th Cir. 1985), and that agencies have broad discretion in selecting the data they need to fulfill the congressional mandate to enforce Title VI through monitoring. Madison-Hughes v. Shalala, 80 F.3d 1121, 1126 (6th Cir. 1996) (noting that “enforcement decisions involve a complicated balancing of a number of factors which are peculiarly within the agency’s expertise, and the agency is far better equipped than the courts to deal with the many variables involved in the proper ordering of its priorities.”) (citing Heckler v. Chaney, 470 U.S. 821, 830–31 (1985)) .
Agency approaches to data collection. Under the authorities described above, many agencies collect data that is helpful in ensuring Title VI compliance. For example, the Federal Transit Administration requires its grant recipients that serve areas with populations over 200,000 to collect and analyze racial and ethnic data showing the extent to which members of minority groups are beneficiaries of programs receiving federal financial assistance, including thepreparation of demographic and service profile maps and charts. FTA Circular 4702.1B, Title VI Requirements and Guidelines for Federal Transit Recipients, ch. IV–7 (August 28, 2012). In addition, FTA requires these recipients to analyze all major service changes to determine their effects on low income and minority communities. Id. Ch. IV–13. These requirements place the responsibility on recipients to analyze their actions, and to collect the data FTA would require in order to check its recipients’ analyses. Similarly, Department of Labor regulations mandate that recipients maintain information required for assessing compliance with the nondiscrimination and equal opportunity provisions of the Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act. 29 C.F.R. §§ 38.41-38.43. The “system and format in which the records and data are kept must be designed to allow … statistical or other quantifiable data analyses to verify the recipient’s compliance ….” Id. § 38.41(b)(1). The Department of Education maintains extensive reporting requirements to ensure that public school districts and elementary and secondary schools are meeting their civil rights obligations. Dep’t of Educ., About the Civil Rights Data Collection (CRDC).[26]
AGENCY PRACTICE TIP
The ready availability of demographic data assists agencies in prioritizing complaint investigations, selecting recipients for compliance reviews, and conducting targeted outreach. Agencies should use this authority to ensure effective enforcement of their disparate impact regulations. Where a recipient does not fully cooperate with an agency’s request for information, and compliance cannot be achieved voluntarily, the agency may refer the matter to the Department of Justice for judicial enforcement. Agencies should consider consider establishing additional requirements for certain recipients to provide information routinely to assist in monitoring compliance with the Title VI disparate impact regulations.
Such Data give recipients themselves a better understanding of the impact of their actions and decisions on protected groups, including the ability to conduct self–assessments of their own compliance with Title VI. For example, in the context of health disparities, HHS has urged its recipients to consider strategies to collect and use racial and ethnic data to help eliminate disparities. Letter from Thomas E. Perez, Director, HHS Office for Civil Rights & David Satcher, Surgeon General, to various recipients (Jan. 19, 2001) (explaining ways in which health care providers can analyze race and ethnicity data to ensure provision of services to minorities, identify differences in the quality of care among various geographic, cultural, and ethnic groups, provide culturally and linguistically appropriate services, and alert recipients to potential Title VI issues). Letter from Dir., Office for Civil Rights, Dep’t Health and Human Servs. and Assistant Sec’y for Health and Surgeon Gen. to President, American Diabetes Assoc. (Jan. 19, 2001) (on file with Dep’t of Justice, Civil Rights Div.).
[1] See , e.g., Anthony G. Greenwald et al., Measuring Individual Differences in Implicit Cognition: The Implicit Association Test , 74 J. Personality & Soc. Psychol. 1464 (1998) (showing that majority of white experiment participants more frequently associate white faces rather than African American faces with “pleasant” factors); Anthony G. Greenwald & Linda Hamilton Krieger, Implicit Bias: Scientific Foundations , 94 Cal. L. Rev. 945, 954– 59 (2006); see also Nilanjana Dasgupta, Implicit Ingroup Favoritism, Outgroup Favoritism, and Their Behavioral Manifestations , 17 Soc. Just. Res. 143 (2004); Gary Blasi, Advocacy Against the Stereotype: Lessons from Cognitive Social Psychology , 49 UCLA L. Rev. 1241 (2002); Jerry Kang, Trojan Horses of Race , 118 Harv. L. Rev. 1489 (2005); Christine Jolls & Cass R. Sunstein, The Law of Implicit Bias , 94 Cal. L. Rev. 969 (2006); Samuel R. Bagenstos, The Structural Turn and the Limits of Antidiscrimination Law , 94 Cal. L. Rev. 1, 5–9 (2006).
[2] Lau was a Title VI case; as noted, Inclusive Communities involved the Fair Housing Act, 42 U.S.C. § 3601 et seq. Cases decided under Title VII or the Fair Housing Act may be instructive. Investigating agencies may find Fair Housing Act case law particularly instructive where the employment context does not present ready analogues. For instance, courts applying the Fair Housing Act frequently examine the impact borne in particular geographic areas, such as neighborhoods, towns, or counties, whereas Title VII cases more frequently involve comparisons between various groups of applicants and employees. Finally, investigating agencies might find helpful guidance from cases decided under an intent theory, but which evaluate statistical evidence of the disparate impact of a policy or practice, including Equal Protection Clause case law. Accordingly, this section will discuss disparate impact discrimination with reference to case law not only under Title VI, but also under these other laws.
[3] See 7 C.F.R. § 15.3(b)(2)–(3) (USDA); 22 C.F.R. § 209.4(b)(2)–(3) (Agency for Int’l Dev.); 15 C.F.R. § 8.4(b)(2)–(3) (Dep’t of Commerce); 45 C.F.R. § 1203.4(b)(2) (Corp. for Nat’l &– Cmty. Serv.); 32 C.F.R. § 195.4(b)(2)(DOD); 34 C.F.R. § 100.3(b)(2)–(3) (Dep’t of Educ.); 10 C.F.R. § 1040.13(c)–(d) (Dep’t of Energy); 40 C.F.R. § 7.35(b)–(c) (EPA); 41 C.F.R. § 101–6.204–2(a)(2)–(3) (GSA); 45 C.F.R. § 80.3(b)(2)–(3) (HHS); 6 C.F.R. § 21.5(b)(2)–(3) (DHS); 24 C.F.R. § 1.4(b)(2)(i)–(3) (HUD); 43 C.F.R. § 17.3(b)(2)–(3) (Dep’t of the Interior); 28 C.F.R. § 42.104(b)(2)–(3)(DOJ); 29 C.F.R. § 31.3(b)(2)–(3) (DOL); 14 C.F.R. § 1250.103–2(b) (NASA); 45 C.F.R. § 1110.3(b)(2)–(3) (Nat’l Found. on the Arts &– Humanities); 45 C.F.R. § 611.3(b)(2)–(3) (NSF); 10 C.F.R. § 4.12(b)–(c) (NRC); 5 C.F.R. § 900.404(b)(2) (OPM); 22 C.F.R. § 141.3(b)(2) (Dep’t of State); 18 C.F.R. § 1302.4(b)(2)–(3) (TVA); 49 C.F.R. § 21.5(b)(2)–(3) (DOT); 31 C.F.R. § 22.4(b)(2) (Dep’t of Treasury); 38 C.F.R. § 18.3(b)(2)–(3) (VA); 18 C.F.R. § 705.4(b)(2) (Water Resources Council).
[4] The Department of Justice issued its discriminatory effect regulation in 1966. 31 Fed Reg. 10,265 (July 29, 1966). Congress, fully aware of this administrative interpretation, has never altered it. Guardians Ass’n v. Civil Serv. Comm’n , 463 U.S. 582, 620–21 (1983) (Marshall, J., dissenting) (noting, among other things, that Congress has enacted ten additional statutes modeled on Title VI “none of which define discrimination to require proof of intent” and that “Congress has not acted to correct any misinterpretation of its objectives despite its continuing concern with the subject matter”).
[5] Memorandum from the Assistant Attorney General to heads of Departments and Agencie s that Provide Federal Financial Assistance (Jul. 14, 1994), available at http://www.justice.gov/ag/attorney–g eneral–july–14–1994– memorandum–use–disparate–impact–standard–administrative–regulations .
[6] Memorandum from the Assistant Attorney General to the Heads of Departmental Agencies, General Counsels, and Civil Rights Directors (Oct. 26, 2001) available at http://www.justice.gov/crt/about/cor/lep/Oct26Memorandum.php ); see Sandoval , 532 U.S. at 281 (assuming for purposes of deciding the case “that regulations promulgated under § 602 of Title VI may validly proscribe activities that have a disparate impact on racial groups ….”).
[7] The test has been codified in Title VII at 42 U.S.C. § 2000e–2(k).
[8] Dep’t of Educ., Dear Colleague Letter on the Nondiscriminatory Administration of School Discipline (Jan. 8, 2014), available at http://www2.ed.gov/about/offices/list/ocr/letters/colleague –201401–title–vi.html.
[9] If statistics are used to establish disparity, they must establish statistically significant disparity, as discussed below in section C.3.c.
[10] E.g. , S. Camden Citizens in Action v. N.J. Dep’t of Envtl. Prot. , 145 F. Supp. 2d 446, 487 opinion modified and supplemented, 145 F. Supp. 2d 505 (D.N.J.) (discussing the methods used to “evaluate the ‘adversity’ of the impact” and considering whether the impacts at issue were “sufficiently adverse” to establish a prima facie case), rev’d on other grounds, 274 F.3d 771 (3d Cir. 2001).
[11] The DOJ regulations quoted here are similar to those of other agencies.
[12] Of course, the challenged policy must be ripe for review by the investigating agency. Where the recipient has not yet adopted the policy because, for instance, several potential options are under consideration, it may be premature to analyze a challenge to that potential policy.
[13] EPA Investigative Report for Title VI Admin. Complaint File No. 16R ‐ 99 ‐ R9 (Aug. 25, 2011), available at http://www.epa.gov/TitleVIcases/ir-082511.pdf.
[14] The factors listed in Villanueva are not intended to be exclusive. There are multiple other potentially relevant factors that affect whether a school closing may violate Title VI. Some of the relevant factors, for example, are noted in the Department of Education’s “Dear Colleague” letter on resource comparability. See http://www2.ed.gov/about/offices/list/ocr/letters/colleague –resourcecomp–201410.pdf .
[16] The Darensburg complaint was brought under state law (California Government Code §11135), which contains language comparable to Title VI and provides explicitly for a private right of action. The court analyzed the prima facie case under Title VI and Title VII standards.
[17] Uniform Guidelines for Employee Selection Procedures. See 29 C.F.R. pt. 1607 (EEOC); 28 C.F.R. § 50.14 (DOJ); and 29 C.F.R. ch. 60–3 (DOL).
[18] Available at https://www2.ed.gov/offices/OCR/archives/pdf/TestingResource.pdf .
[20] The report is available at https://perma.cc/KP2X-JXFQ (last visited Nov. 18, 2016).
[21] The Circular is available at http://www.fta.dot.gov/documents/FTA_Title_VI_FINAL.pdf.
[22] This letter is available at https://perma.cc/5S4E-L8J6 .
[24] Letter from Assistant Attorney General to Director of North Carolina Administrative Office of the Courts (Mar. 8, 2012), available at https://perma.cc/69Q6-NALT .
[25] These accountability requirements are not unique to federal financial assistance from DOJ but rather are a universal feature of the grant–making system. Every agency that has promulgated Title VI regulations includes similar or identical accountability requirements. See 7 C.F.R. § 15.5(b) (USDA); 22 C.F.R. § 209.6(b) (USAID); 15 C.F.R. § 8.7(b) (Dep’t of Commerce); 45 C.F.R. § 1203.6(b) (Corp. for Nat’l and Community Serv.); 32 C.F.R. § 195.7(b) (DOD); 34 C.F.R. § 100.6(b) (Dep’t of Educ.); 10 C.F.R. §1040.89–3 (Dep’t of Energy); 40 C.F.R. § 7.85 (EPA); 41 C.F.R. § 101–6.29–3 (GSA); 45 C.F.R. § 80.6(b) (HHS); 6 C.F.R. § 21.9 (DHS); 24 C.F.R. § 1.6(b)(HUD); 43 C.F.R. § 17.5(b) (Dep’t of the Interior); 29 C.F.R. § 31.5(b) (DOL); 14 C.F.R. § 1250.105(b) (NASA); 45 C.F.R. § 1110.6 (Nat’l Found. on the Arts and Humanities); 45 C.F.R. § 611.6(b) (NSF); 10 C.F.R. § 4.33 (NRC); 5 C.F.R. § 900.406 (OPM); 13 C.F.R. § 112.9(b) (SBA); 22 C.F.R. § 141.5(b) (Dep’t of State); 18 C.F.R. § 1302.6(b) (TVA); 49 C.F.R. § 21.9(b) (DOT); 38 C.F.R. § 18.6(b) (VA); 18 C.F.R. § 705.6(b) (Water ResourcesCouncil).